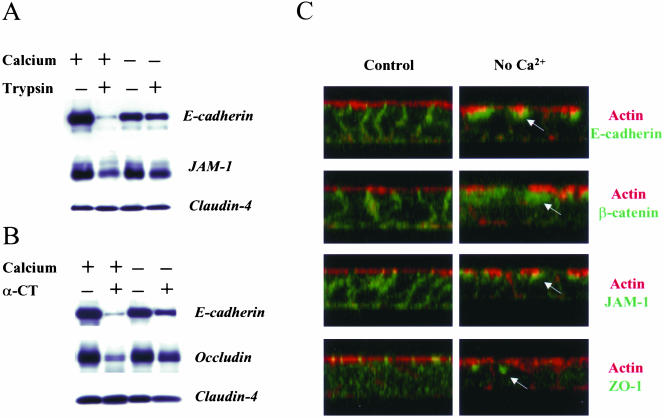
Figure 1.
Depletion of extracellular calcium decreases proteolytic sensitivity of AJ and TJ proteins by inducing their translocation into a subapical intracellular compartment. Confluent T84 monolayers were incubated in either complete T84 medium or in calcium-free S-MEM for 120 min followed by brief exposure to (A) trypsin (0.05%) or (B) α-chymotrypsin (α-CT; 0.5%) solutions as described in MATERIALS AND METHODS. Thereafter, cells were lysed and amounts of junctional proteins in total cell lysates determined by Western blotting. In Panel C, another subset of control and calcium-depleted T84 monolayers was fixed, double-labeled with actin and E-cadherin, β-catenin, JAM-1, or ZO-1, and analyzed by confocal microscopy (x-z images). Calcium depletion decreases the sensitivity of E-cadherin, JAM-1, and occludin to proteolysis indicating internalization of these proteins. Reconstructed confocal images in the x-z plane reveal internalization of E-cadherin, β-catenin, JAM-1, and ZO-1 into a subapical cytosolic compartment located under the apical F-actin (arrows).