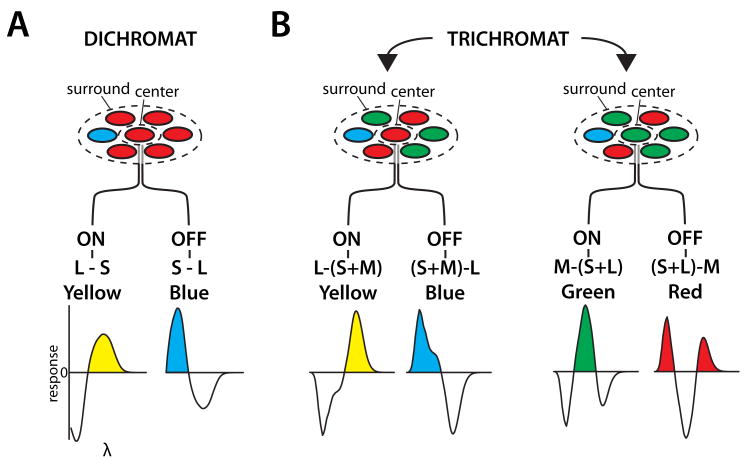
Fig. 7.
A) In a dichromat, midget ganglion cells with an S cone in the surround could provide the basis for blue-yellow color vision with yellow percepts being mediated by ON ganglion cells and blue percepts mediated by OFF ganglion cells. Spectral response properties of each of the two spectrally opponent cells types are plotted. B) The addition of a third cone type to the retina transforms the former blue and yellow pathways. What was a single S vs. L receptive field type is transformed into two different receptive fields, one with an L cone center and one with an M cone center. ON and OFF pathways split the L center receptive fields into L-(S+M) and (S+M)-L and the M center pathways into M-(S+L) and (S+L)-M. The spectrally opponent response properties of each of the four trichromatic ganglion cell types is shown. The cells responsible for red, green, blue and yellow are all derived from a blue-yellow ancestor, but they all differ significantly from the preexisting blue yellow system.