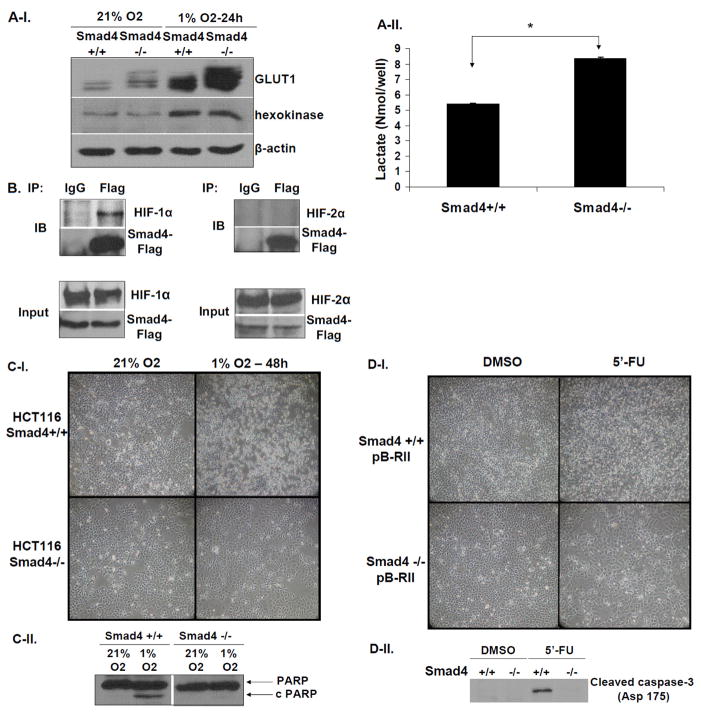
Figure 5. SMAD4 deficiency correlates with increased GLUT1 levels and resistance to hypoxia-induced cell death and 5′-fluorouracil treatment.
A-I. Loss of SMAD4 increases GLUT1 protein levels. Western blotting for detection of GLUT1 protein levels in protein lysates isolated from HCT116 SMAD4+/+ and SMAD4−/− grown under normoxic (21% O2) or hypoxic (1% O2) conditions for 24h. A-II. Lactate secretion from HCT116 SMAD4+/+ and SMAD4−/− cells growing under normoxic conditions. B. Smad4 physically interacts with HIF1α but not with HIF2α under hypoxic conditions. HCT116 SMAD4+/+ cells were transiently co-transfected with PRK5-SMAD4-Flag and pCDNA3-HIF1αAA vectors or PRK5-SMAD4-Flag and pCDNA3-HIF2αAA vectors, respectively, for 16h and cultured under hypoxic conditions for an additional 5h. Total cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with mouse IgG antibody (mock) or mouse anti-Flag antibody and immunoprecipitates were analyzed by Western blotting to detect either HIF1α or HIF2α. C. Representative examples of light microscopy images (C-I) and Western blotting for detection of the cleaved PARP (C-II) in HCT116 SMAD4+/+ and SMAD4−/− grown in normoxic (21% O2) or hypoxic conditions (1% O2). D. Representative examples of light microscopy images (D-I) and Western blotting for detection of the cleaved caspase-3 (Asp 175) (D-II) from total cell lysates of HCT116 SMAD4+/+ and SMAD4−/− cultures which were either treated with either mock (DMSO) or 5′-fluorouracil (5′-FU) (1μg/ml) for 72h.