Figure 1.
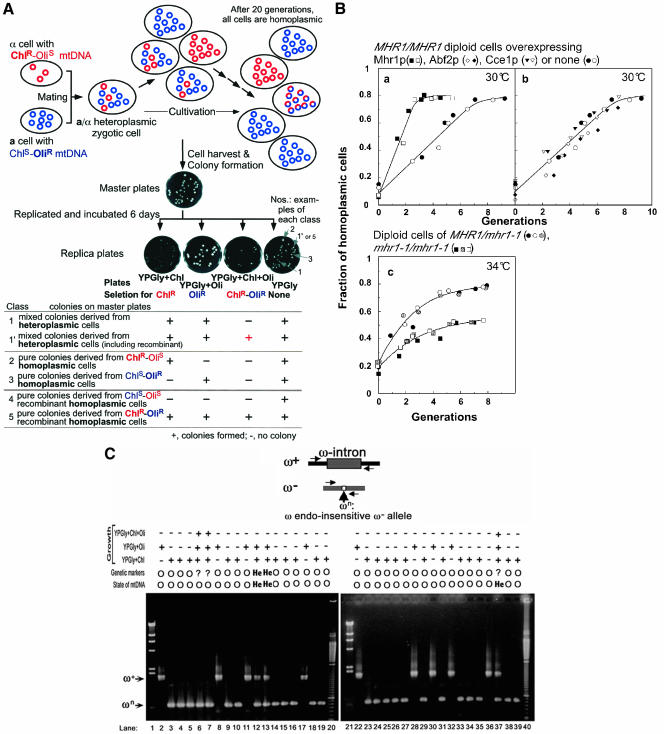
Active roles of Mhr1p in vegetative segregation to generate homoplasmic cells. (A) The concept of vegetative segregation and homoplasmy, and a genetic assay for homoplasmy. Heteroplasmic cells are generally created by a mutation, and in yeasts and fungi (not in mammals), they are reproducibly created by mating cells with different sets of mitochondrial alleles, as shown in this figure. Unlike the nuclear alleles, which are segregated at 1:1 mostly through meiosis (Mendelian segregation), all alleles are segregated during 10–20 generations of vegetative growth, and finally, in each of the progeny, all of the mtDNA copies have the same sequence (the same set of alleles). In this study, heteroplasmic cells were obtained by mating α-cells (mt[ChlR-OliS] and a-cells (mt[ChlS-OliR], and only diploid zygotes were allowed to grow at 30°C or 34°C. Samples of the culture were withdrawn, diluted, and spread on SD plates to form colonies. The colonies on the master plate were replicated onto four YPGly plates, with or without chloramphenicol and/or oligomycin. The colonies on the master plates were classified according to the criteria shown in the Table in this figure, and the total fraction of colonies in classes 2 through 4 among all of the colonies was calculated as the fraction of homoplasmic cells. Colonies of class 5 homoplasmic cells cannot be distinguished from those in class 1′ heteroplasmic cells by this assay, but the fraction was very small and can be ignored within the first five generations (see text). YPGly+X indicates a YPGly plate supplemented with antibiotics X (Chl and Oli indicate chloramphenicol and oligomycin, respectively). +, cells form colonies; -, cells do not form colonies. Circles represent each unit size mtDNA copy. Blue symbols and red symbols represent mtDNA (or alleles) derived from a-cells (mt[ChlS-OliR] and mtDNA (or alleles) derived from α-cells (mt[ChlR-OliS], respectively. Circles with a red part and a blue part represent a unit size copy of recombinant mtDNA. (B) A genetic assay for mtDNA homoplasmy, and the effects of the in vivo activity of Mhr1p on vegetative segregation. The calculated fractions of homoplasmic cells are plotted against the generation time of zygotes at 30°C or 34°C. Closed, shadowed, crossed, slashed, and open symbols indicate data from independent experiments. Each panel contains at least two independent series of experiments. a and b, cells overexpressing the indicated protein at 30°C in GalSR medium. Circles, diploids of parental strains (YKN1423/pYES2 × W303a-187); squares, diploids overproducing Mhr1p (YKN1423/pYESMHR1 × W303aGalMHR1); inverted triangles, diploids overproducing Cce1p (W303aGalCCE1 × W303a GalCCE1); diamonds, diploids overproducing Abf2p (W303aGalABF2 × W303a Gal-ABF2). Cells without an overexpression plasmid grew with a generation time of ∼1.2 h without a lag at 30°C. c, cells grown at 34°C in SD medium. Circles, MHR1/mhr1-1 diploids (YKN1423 × FL67-2c); squares, mhr1-1/mhr1-1 diploids (FL67-1423 × FL67--2c). The cells grew with a generation time of 1.2 h for both MHR1/mhr1-]1 cells and mhr1-1/mhr1-1 cells, without any apparent lag. (C) A PCR assay for mtDNA homoplasmy. Thirty-two colonies of diploid cells, derived from a cross between YKN1423 (α, ω+, Oli1R) and 55R5-C1(a, ωn, Chl321R) cells, were randomly selected from the master plate. Cells from each colony were propagated and whole cellular DNA was prepared. The DNA fragments containing the ω locus were amplified by PCR and were analyzed by electrophoresis. At the top, schematic physical maps at the ω+ (contains the ω-intron) and ω- (ω-intron-less) loci on mtDNA are indicated. ωn is a cis mutation at the ω- locus that prevents the cleavage by the ω endonuclease. Pairs of horizontal arrows in the drawing indicate the primers used for PCR. Homoplasmic or heteroplasmic cells, as determined by the genetic assay and the PCR-based DNA assay, are indicated as O (homoplasmic), He (heteroplasmic), and? (uncertain). Lanes 4–19 and lanes 24–39, yeast DNA samples. Controls, lanes 2 and 22, YKN1423 (ω+, Oli1R); lanes 3 and 23, 55R5-C1(ωn, Chl321R). Lanes 1 and 21, λ DNA HindIII-digests; lanes 20 and 40, 100-bp DNA ladder. Arrows indicate the positions of ω+ and ωn.