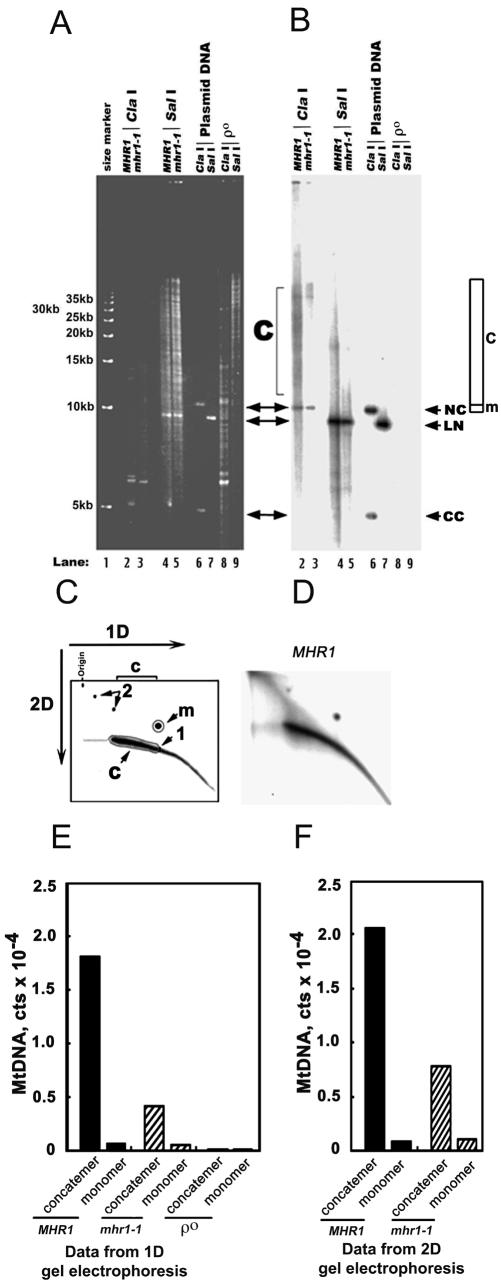
Figure 2.
mhr1-1 prevents concatemer formation at 34°C. (A and B) One-dimensional gel electrophoretic analysis of mt-pMK2 DNA. The MHR1 (lanes 2 and 4) and mhr1-1 (lanes 3 and 5) cells with t-pMK2 DNA (AFS98-pMK2 [MHR1] and AFS984a-pMK2 [mhr1-1]) and ρ0 cells (mtDNA-less cells; AFS98 ρ0; lanes 8 and 9) were grown in YPD at 34°C from 1.0 × 105 cells/ml to 5.0 × 107 cells/ml. Whole DNA was isolated and treated with the restriction endonuclease ClaI (no cleavage site in pMK2 DNA; lanes 2, 3, and 8) or the restriction endonuclease SalI (a single cleavage site in pMK2 DNA; lanes 4, 5, and 9). Then, the treated DNA was analyzed by one-dimensional electrophoresis as described previously (Lockshon et al., 1995; Ling and Shibata, 2002). CC, closed circular monomer; LN, linear monomer; NC and m (region), nicked circular monomer; c (region), concatemers. Lanes 6 and 7, the isolated plasmid pMK2 DNA treated with the restriction endonucleases ClaI and SalI, respectively. Lane 1, 5-kb ladder as a size marker. (A) Gel stained with ethidium bromide. (B) Signals from mt-pMK2 DNA obtained by Southern hybridization by using the [32P]pMK2 DNA-probe. (C and D) Two-dimensional gel electrophoretic analysis of mt-pMK2 DNA. Whole cellular DNA was isolated and treated to digest the nuclear chromosomal DNA by the restriction endonuclease ClaI (no cleavage site in pMK2 DNA) as described in A and B. The mt-pMK2 DNA was detected by Southern hybridization by using the [32P]pMK2 DNA-probe, after separation by size in the first dimensional electrophoresis and by shape in the second dimensional run. (C) Schematic diagram; 1, linear monomer; m (area), nicked circular monomer; 2, circular multimers; c (area), linear concatemers (see Backert, 2002 for the assignments of DNA species); 1D, the first dimensional run; 2D, the second dimensional run. (D) The two-dimensional gel profile of the mt-pMK2 DNA isolated from MHR1 cells grown at 34°C. (E and F) Quantification of the signals in one-dimensional and two-dimensional gels. Based on the Southern hybridization experiment, the 32P signals from circular monomers (indicated as monomer) and linear concatemers (indicated as concatemer) in B and D were plotted. The overlap of signals from linear DNA with the signals from circular monomers in 1D gel electrophoresis (E) was corrected as described in the MATERIALS AND METHODS. The absolute numbers of the signals of each DNA species varied between the experimental series, but the relative signals of concatemers to circular monomers were reproducible as follows: the ratio of concatemers to circular monomers was 27.2 ± 1.8 in the MHR1 cells and 7.8 ± 0.5 in the mhr1-1 cells (each calculated from two independent experiments by using one-dimensional gels, and two independent experiments using two-dimensional gels). Concatemer, linear concatemeric mt-pMK2 DNA; monomer, circular monomers of mt-pMK2 DNA.