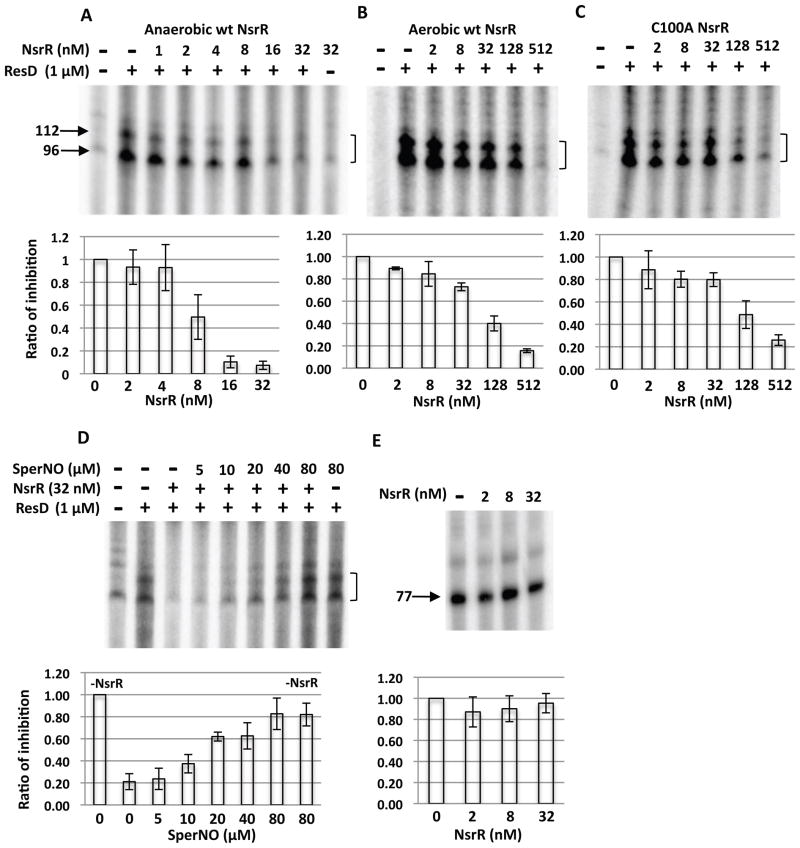
Figure 5.
In vitro transcription of nasD. The nasD template (−170 to +96) was incubated without or with σARNAP, ResD∼P (1 μM) and increasing concentrations of wild-type NsrR-His6 purified under anaerobic conditions (A), aerobic conditions (B) or C100A mutant NsrR (C). An arrow with numbers shows the size of transcript in nucleotides. A bracket shows two nasD transcripts (96 and 112 base) that are generated by transcription in vitro as previously described (Geng et al., 2004) and the 96-base transcript corresponding to RNA transcribed in vivo.
D. Effect of spermine NONOate on repressor activity of NsrR. SperNO at the indicated concentration was added in the reaction with anaerobically purified NsrR.
E. In vitro transcription of rpsD using anaerobically purified NsrR. The 77 base transcript is marked.
The intensity of the corresponding bands was quantified with ImageJ and is shown as the ratio of transcript level in the presence of NsrR to that in the absence of NsrR (A, B, C and E), or as the ratio of transcript level in the presence of NsrR (and SperNO) to that in the absence of NsrR/SperNO (D). The average values (n=6 for A and n=3 for the rest) are shown with standard deviation.