Figure 5.
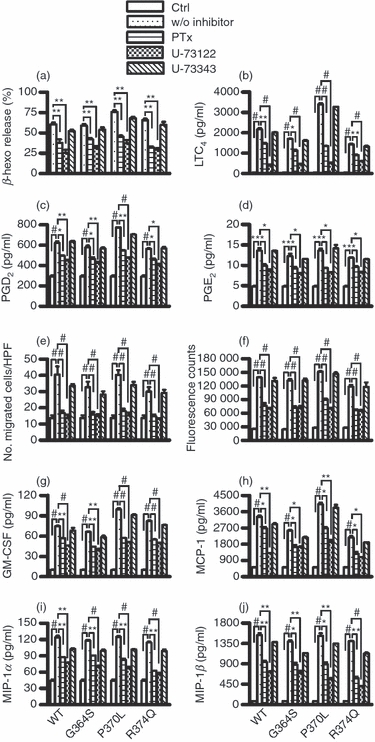
Inhibitory effects of pertussis toxin and U-73122 on catestatin-induced mast cell activation. Cells were pre-treated with 1000 ng/ml pertussis toxin (PTx), 10 μm U-73122, 10 μm U-73343 or 0·1% DMSO for 2 hr. (a) Pre-treated cells (2 × 105 cells) were stimulated with 2·5 μm wild-type catestatin (WT), Gly364Ser (G364S) or Pro370Leu (P370L), 5 μm Arg374Gln (R374Q), or diluent 0·01% acetic acid (Ctrl, control) for 40 min, and β-hexosaminidase (β-Hexo) release was measured. (b–d) Pre-treated cells (1 × 106 cells) were also stimulated with 10 μm WT catestatin, G364S, P370L, R374Q, or 0·01% acetic acid (Ctrl, control) for 30 min, and the release of leukotriene (LT) C4, prostaglandin (PG) D2, and PGE2 was assessed by an enzyme immunoassay. (e) In addition, pre-treated cells were incubated with 0·32 μm WT catestatin, G364S, P370L, R374Q, or 0·01% acetic acid (Ctrl, control) for 3 hr, and the chemotaxis assay was then performed. (f) Cells were also evaluated for intracellular Ca2+ mobilization following stimulation with 5 μm WT catestatin, G364S, P370L, R374Q, or 0·01% acetic acid (Ctrl, control). Furthermore, cells were stimulated for 6 hr with 10 μm WT catestatin, G364S, P370L, R374Q, or 0·01% acetic acid (Ctrl, control), and the levels of (g) granulocyte–macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF), (h) monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1/CCL2), (i) macrophage inflammatory protein-1α (MIP-1α/CCL3) and (j) MIP-1β/CCL4 released into the supernatants were determined by an ELISA. Values are the mean ± SD of four to nine separate experiments. **P < 0·01 and #P < 0·001 for comparisons between untreated cells (Ctrl, control) and stimulated groups without inhibitor (w/o inhibitor). *P < 0·05, **P < 0·01, and #P < 0·001 for comparisons between the presence and absence of inhibitors.
