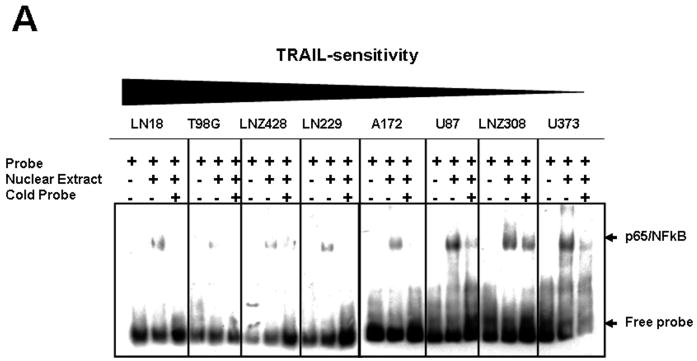
Figure 4. Bortezomib inhibits NF-κB DNA-binding activity in glioma cell lines.
(A). Nuclear extract was prepared from eight established malignant human glioma cell lines. NFκB DNA-binding was assessed by electrophoretic mobility shift assay (EMSA) as described in the Materials and Methods. (B). LN18, U87, LNZ308, and U373 cells were seeded at 60% confluence, allowed to attach overnight. Cells were treated with varying concentrations of bortezomib for 24 h. Nuclear extracts were prepared, and NF-κB DNA-binding activity was measured as described in the Materials and Methods. The values represent the mean ± standard deviation for two separate experiments performed in triplicate (*p < 0.05; **p < 0.005, bortezomib treated versus untreated control). (C). Glioma cells were treated with varying concentrations of bortezomib for 24 h. Cell extracts were prepared, and equal amounts of protein were separated by SDS-PAGE and subjected to Western blotting analysis and densitometric measurement was performed as described in the Materials and Methods. (D). LNZ308 and U373 were treated with TRAIL (5ng/ml) or bortezomib (5nM) or the combination of both for 24 h. NF-κB DNA-binding was assessed by electrophoretic mobility shift assay (EMSA) as described in the Materials and Methods.