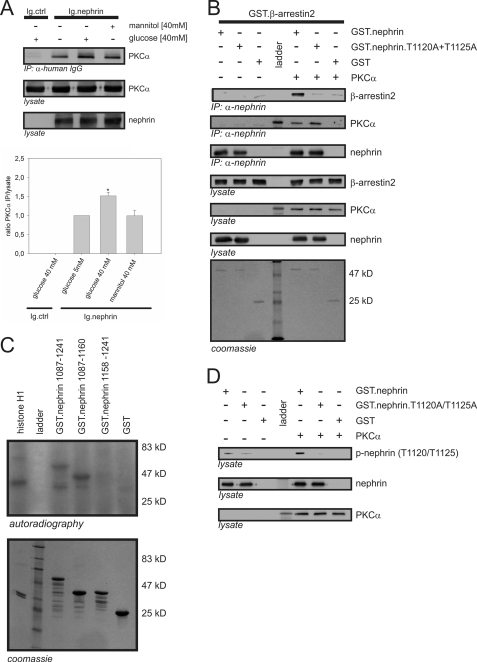
FIGURE 3.
Interaction of β-arrestin2 with nephrin in vitro depends on PKCα phosphorylation of nephrin threonine residues 1120 and 1125. A, Western blots showing coimmunoprecipitation in HEK293T cells overexpressing untagged PKCα (PKCα), Ig-tagged nephrin C terminus (Ig.nephrin), or Ig tag as the negative control (Ig.ctrl). The cells were maintained in 5.5 or 40 mm glucose or 40 mm mannitol (osmotic control) for 24 h. Then coimmunoprecipitation with Ig.ctrl or Ig.nephrin was performed. The level of interaction was determined by staining of PKCα. The results of three independent experiments were quantified by densitometry and graphed as the ratio of the PKCα (immunoprecipitation, IP) signal intensity to the lysate signal intensity (ratio PKCα immunoprecipitation/lysate). The data are the means ± S.E. *, p < 0.05 (Student's t test. B, in vitro pull-down assay. Aliquots of recombinant nonmutated nephrin cytoplasmic domain (GST.nephrin), double-mutant cytoplasmic domain (GST.nephrin.T1120A+T1125A), and control protein (GST) expressed in E. coli were immobilized by anti-nephrin antibody in the presence or absence of PKCα. In the Western blots, the interaction of nephrin with β-arrestin2 and PKCα was determined by staining with specific antibodies. Lysate controls show protein input of β-arrestin2, PKCα, and nephrin. Coomassie staining of SDS-PAGE gel showed equal protein input of Ig.nephrin (51 kDa) and GST (25 kDa). The molecular mass markers are indicated in kDa. C, in vitro phosphorylation assay. Aliquots of recombinant wild-type nephrin cytoplasmic domain (amino acids 1087–1241) and truncated nephrin cytoplasmic domain with (amino acids 1087–1169) and without the predicted β-arrestin2 interaction site (amino acids 1158–1241) were expressed in E. coli. Then recombinant PKCα and γ-32P were added. Histone H1 was used as the positive control. Phosphorylation was visualized by autoradiography. Coomassie staining of an SDS-PAGE gel showed equal protein input. Molecular mass markers are indicated in kDa. D, in vitro phosphorylation assay with phospho-nephrin antibody. Aliquots of recombinant nonmutated nephrin cytoplasmic domain (GST.nephrin), double-mutant cytoplasmic domain (GST.neprin.T1120A+T1125A), and control protein (GST) expressed in E. coli were immobilized by anti-nephrin antibody in the presence or absence of PKCα. In the Western blots, phosphorylation of nephrin, the mutant, and the control was visualized by staining with phospho-nephrin antibody to recognize phosphorylated nephrin threonine residues 1120 or 1125. Staining of total nephrin and PKCα served as the internal loading control.