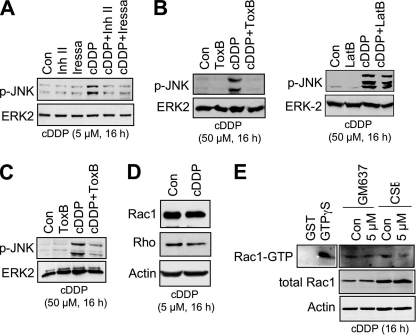
FIGURE 6.
Cisplatin-induced activation of SAPK/JNK requires tyrosine kinases and Rho GTPases. A, human CSB-defective cells were left untreated (Con) or were exposed to cisplatin (5 μm). 8 h after addition of cisplatin, tyrosine kinase inhibitors targeting Bcr-Abl (Inh II) (10 μm) (91) or EGFR (Iressa) (10 μm) were added. After a further incubation period of 8 h in the presence of inhibitor and cisplatin, cells were harvested for analysis of SAPK/JNK phosphorylation (p-JNK). B, human GM637 fibroblasts were pretreated for 2 h with either Rho-inactivating ToxB (2.5 ng/ml) (left panel) or latrunculin B (LatB) (1 μm) (right panel), which disrupts F-actin filaments. Afterward, cDDP was added (50 μm), and cells were further incubated for 16 h before the phosphorylation status of SAPK/JNK (p-JNK) was analyzed by Western blot analysis. C, primary human fibroblasts were pretreated with Rho-inactivating clostridial ToxB (1 ng/ml) for 2 h. Afterward, cDDP (50 μm) was added, and cells were harvested 16 h later for determination of SAPK/JNK activation (p-JNK) by Western blot. D, 16 h after continuous cisplatin treatment (5 μm) of human CSB-defective cells (CSB), the expression of the Rho GTPase Rac1 and RhoA-like GTPases (Rho) was analyzed in the membrane fractions. E, 16 h after permanent cisplatin (5 μm) treatment of CSB-proficient (GM637) and CSB-defective human cells (CSB), the GTP binding status of Rac1 (Rac1-GTP) was analyzed by GST-PAK pulldown experiments as described under “Experimental Procedures.” As internal controls, protein expression of β-actin (Actin) and total Rac1 were determined in total cell extracts. GST, pulldown using GST (negative control); GTPγS, GST-PAK pulldown using cell extract preincubated with GTPγS (positive control).