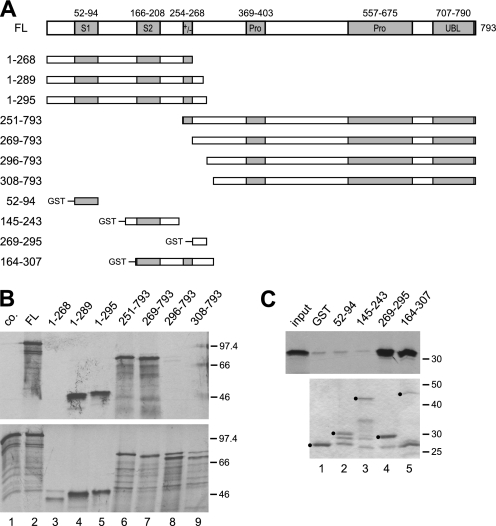
FIGURE 1.
A short region immediately C-terminal to the charged region of SF3a120 is sufficient for SF3a66 binding. A, scheme of in vitro-translated and GST-tagged SF3a120 proteins. Boxes indicate known protein domains as follows: S1 and S2, SURP1 and SURP 2 motifs; +/−, charged region; Pro, Pro-rich regions with PXPP motifs. Numbering above full-length SF3a120 (accession no. Q15459) refers to amino acids. Numbers on the left refer to N and C termini of SF3a120 mutants. B, GST pulldown of N- and C-terminal SF3a120 deletion mutants with GST-3a66/1–216. In vitro-translated SF3a120 proteins indicated above the figure were incubated with GST (lane 1) or GST-3a66/1–216 (lanes 2–9) bound to glutathione-agarose. Only 3a120-FL was incubated with the GST control (lane 1, co.). Bound proteins (top) and 20% of the input proteins (bottom) were separated by 10% SDS-PAGE and visualized by autoradiography. The migration of protein markers is indicated in kDa to the right of each panel. C, GST pulldown with proteins corresponding to internal segments of SF3a120. GST (lane 1) or GST-tagged SF3a120 proteins (as indicated above lanes 2–5) were bound to glutathione-agarose and incubated with in vitro-translated 3a66-FL (input, first lane in top panel; 20% of input is shown). Bound proteins were separated by 10% SDS-PAGE and detected by autoradiography (top). GST-tagged proteins used were separated in a 10% SDS gel and stained with Coomassie Blue (bottom). Full-length proteins are marked with black circles.