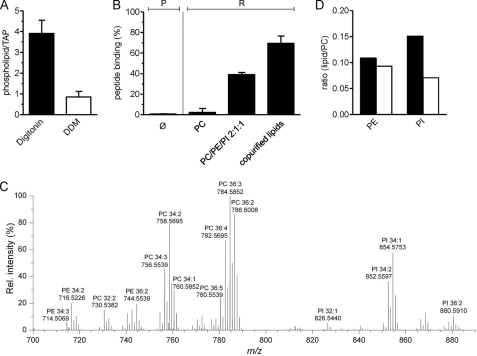
FIGURE 7.
Associated lipids modulate TAP function. A, DDM causes delipidation of the TAP complex. After purification in digitonin or DDM, TAP-associated phospholipids were determined via the amount of inorganic phosphate. Each data point represents the mean value of triplicate measurements. B, recovery of peptide binding activity after reconstitution. DDM-purified TAP was reconstituted into liposomes prepared of DOPC; PC was doped with PE and PI lipids (soybean polar extract) or into lipids extracted after purification with digitonin. Peptide binding to purified (P) and reconstituted TAP (R) was analyzed, compared with DDM-purified TAP (Ø), and normalized to protein orientation as determined by TEV cleavage. C, after purification in digitonin, TAP-associated lipids were profiled by LC FT-MS (representative spectrum, positive ion mode). Identified lipid species are annotated by m/z, and sum composition (total carbon atoms in acyl chains:double bonds) is shown. D, comparison of PE/PC and PI/PC intensity ratios from the TAP complex (black bars) and in total cell extracts (white bars). Error bars in A and B show S.D. Rel. intensity, relative intensity.