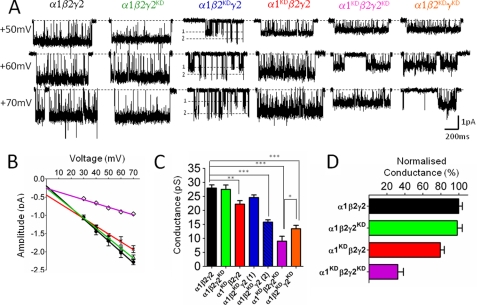
FIGURE 5.
Charge reversal mutations in the extracellular domain affect outward conductance of the α1β2γ2 GABAA receptor. α1, β2, and γ2 subunits were expressed in HEK cells at a 1:1:4 ratio. A shows representative outward currents recorded in the cell-attached configuration at several voltages from wild-type and mutant receptors (display fc = 1 kHz). Each mutant subunit carries two charge reversal mutations (KK to DD) at homologous position to Asp-97 of the α1 Torpedo (see text). Conductance values are reported in Table 5. B, current-voltage plots for representative mutant and wild-type receptors. α1β2γ2 (black line, ●), α1KDβ2γ2 (red line, x), α1 β2γ2KD (green line, Δ), α1KDβ2γ2KD (violet line and ♢). C, conductance values for all subunit combination shown as bar graph. Introduction of charge reversal mutations at homologous positions in the α1, β2, or γ2 subunit decreases conductance in a subunit-specific manner. Asterisks denote the significance after a one-way ANOVA test followed by Dunnett's test. D, bar graph of outward conductance values normalized for their wild type. The γ2 subunit does not affect conductance when it is the only subunit carrying the charge reversal mutation. However, note the γ2 mutation decreases synergistically conductance in combination with mutations in either the α1 or the β2 subunit.