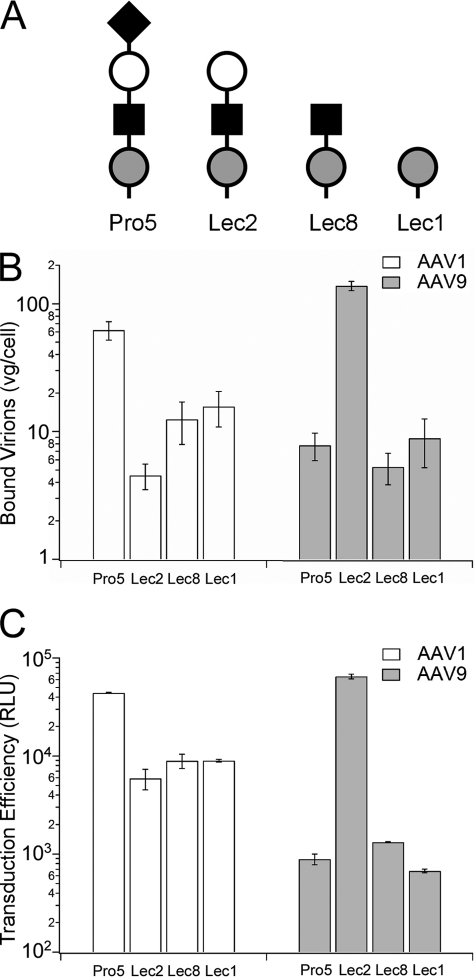
FIGURE 2.
Effect of glycan chain composition on cell surface binding and transduction of AAV9. A, schematic representation of N-glycan compositions of the parental CHO Pro5 cell line and mutants Lec2, Lec8 and Lec1 (36) using nomenclature proposed by the Consortium for Functional Glycomics nomenclature committee (●, mannose; ■, GlcNAc; ○, galactose; ♦, sialic acid) is shown. B, binding of AAV1 (white bars) and AAV9 (gray bars) particles to wild-type and parental CHO cell lines was analyzed using quantitative PCR as described under “Materials and Methods.” The number of bound virions is expressed as vg/cell. C, transduction efficiency (relative light units, RLU) of AAV1 (white bars) and AAV9 (gray bars) particles (m.o.i. = 1000 vg/cell) on parental and mutant CHO cell lines was analyzed by quantifying luciferase transgene expression at 24 h after infection. All binding experiments were carried out in quadruplicate and infectivity assays in triplicate. Error bars represent S.E.