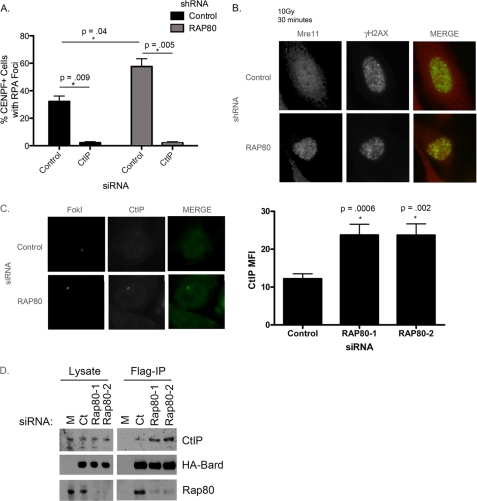
FIGURE 5.
Loss of RAP80 results in increased accumulation of Mre11- and CtIP-dependent nuclease activity at breaks. A, cells expressing control or RAP80 shRNA were treated with control or CtIP siRNA, analyzed for RPA focus formation in CENPF-positive cells. CtIP is necessary for the increase in RPA focus formation observed following RAP80 knockdown. Error bars, S.E. of two independent experiments. p values were calculated in comparison with control siRNA-treated cells. B, cells expressing control or RAP80 shRNA were irradiated, fixed after 30 min, and evaluated for Mre11 focus formation following IF. Cells treated with RAP80 knockdown showed an increase in Mre11 focus formation. C, U2OS reporter cells were treated with control or RAP80 siRNA, transduced with FokI, and analyzed for CtIP recruitment to FokI-induced DSBs. Loss of RAP80 led to an increase in CtIP accumulation at damage sites, quantified on the right. Error bars, S.E. of two independent experiments. D, S3 cells expressing FLAG- and HA-tagged BARD1 were transfected with control or RAP80 siRNA. Cell lysates were subjected to FLAG immunoprecipitation (IP) and immunoblotted for CtIP to analyze the BRCA1-CtIP interaction. Loss of RAP80 resulted in increased BRCA1-CtIP complex formation.