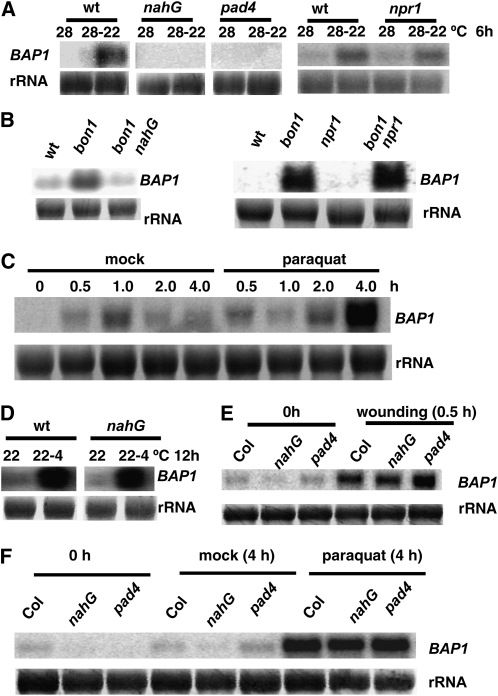
Figure 1.
Induction of BAP1 by multiple stimuli. Shown are BAP1 expressions analyzed by RNA blot. Two-week-old plants grown at 28°C were used for cooling treatment (28°C–22°C). Three-week-old plants grown at 22°C were used for paraquat, SA, and cold (22°C–4°C) treatments. Total RNAs were prepared from tissues collected at indicated time points, and rRNAs were used as the loading controls. A, BAP1 induction by cooling is SA and PAD4 dependent but not NPR1 dependent. BAP1 induction is abolished in nahG and pad4 plants but is present in the npr1 mutant. B, BAP1 induction in bon1 is SA dependent but not NPR1 dependent. The up-regulation of BAP1 in the bon1 mutant is abolished in nahG but is retained in npr1. C, BAP1 is induced by paraquat. Plants were sprayed with a 20 μm paraquat solution containing 0.1% Tween 20 or a mock solution of 0.1% Tween 20. BAP1 expression was greatly induced at 4 h after paraquat treatment. An apparent increase in the 1.0-h mock sample is largely due to an overloading of total RNA. D, BAP1 induction by cold is not SA dependent. BAP1 induction by this cold treatment is present in nahG and pad4. E, BAP1 induction by wounding is not SA or PAD4 dependent. Plants were wounded by a needleless syringe. BAP1 was rapidly induced at 0.5 h after wounding. F, BAP1 induction by paraquat is not SA or PAD4 dependent. BAP1 induction by paraquat is retained in nahG or pad4 mutant. wt, Wild type.