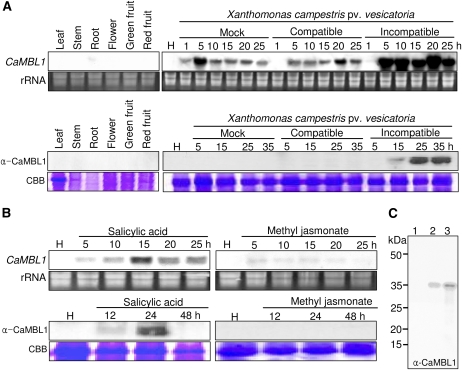
Figure 1.
RNA gel- and western-blot analyses of the expression of CaMBL1 in pepper plants. A, Expression of the CaMBL1 gene and CaMBL1 protein in healthy organs of pepper plants and in pepper leaves at various times after inoculation with the virulent strain Ds1 and the avirulent strain Bv5-4a of Xcv. B, Expression of the CaMBL1 gene and CaMBL1 protein in pepper leaves at various times after treatment with SA (5 mm) and methyl jasmonate (100 μm). Equal loadings (10 μg) of RNA were verified by visualizing rRNA on gels stained with ethidium bromide. Coomassie Brilliant Blue (CBB) staining is shown for the 60-kD region of protein extracts. C, Immunoblot of His-tagged CaMBL1 protein using the anti-CaMBL1 antiserum raised in rabbits against a synthetic peptide corresponding to C-terminal residues 284 to 297 of CaMBL1. His-tagged CaMBL1 proteins expressed in E. coli BL21 was used. Lane 1, Uninduced E. coli BL21 cell extracts (1 μg of protein); lane 2, 0.1 μg of His-tagged CaMBL1 protein expressed in E. coli BL21 cells after isopropylthio-β-galactoside induction; lane 3, 1 μg of His-tagged CaMBL1 protein expressed in E. coli BL21 cells after isopropylthio-β-galactoside induction. [See online article for color version of this figure.]