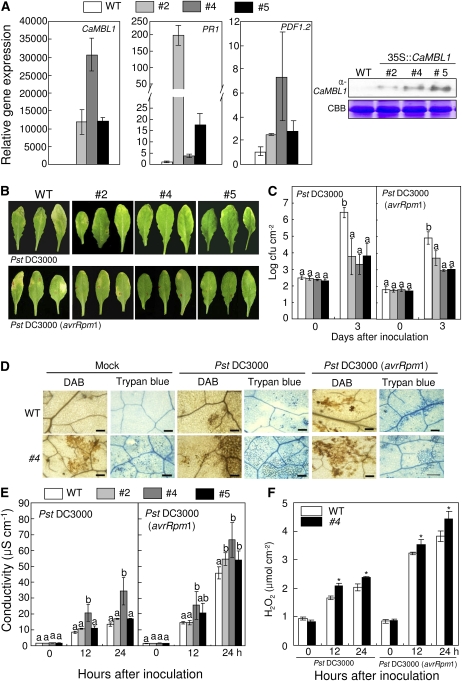
Figure 8.
Enhanced resistance of CaMBL1-OX transgenic Arabidopsis plants to P. syringae pv tomato infection. A, Real-time quantitative PCR and western-blot analyses of the expression of CaMBL1 and Arabidopsis defense-related genes in wild-type (WT) and transgenic plants (lines 2, 4, and 5). Transcript levels were normalized to the expression of pepper 18S ribosomal RNA measured in the same samples. B, Disease symptoms of wild-type and transgenic plants inoculated with Pst DC3000 strains. Leaves of 4-week-old Arabidopsis plants were infiltrated with a suspension (105 cfu mL−1) of Pst DC3000 or Pst DC3000 avrRpm1. Disease symptoms were photographed 5 d after inoculation. C, Bacterial growth in leaves of wild-type and transgenic lines inoculated with Pst DC3000 and Pst DC3000 avrRpm1. D, DAB and trypan blue staining of leaf tissues of wild-type and transgenic plants 24 h after inoculation with Pst DC3000 or Pst DC3000 avrRpm1. Bars = 0.1 mm. E, Quantification of electrolyte leakage from leaf tissues inoculated with Pst DC3000 or Pst DC3000 avrRpm1. Samples were taken 0, 12, and 24 h after inoculation. F, Quantification of H2O2 in wild-type and transgenic plants after inoculation with Pst DC3000 or Pst DC3000 avrRpm1 using the xylenol orange assay. Values are presented as means ± sd. Different letters indicate significant differences from three independent experiments based on the lsd test (P < 0.05). Asterisks indicate significant differences with respect to empty vector control plants (Student’s t test, P < 0.05). [See online article for color version of this figure.]