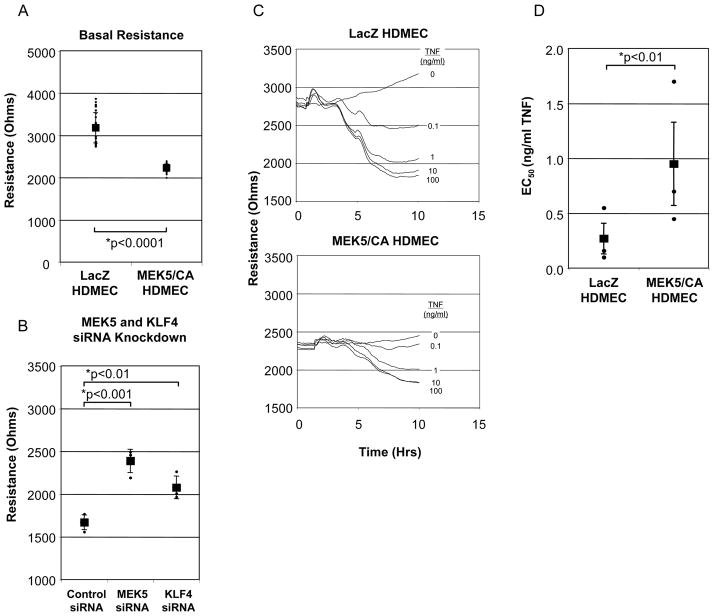
Figure 7. Role of MEK5/CA on Barrier Function and TNF-induced Vascular Leak.
A) LacZ and MEK5/CA HDMEC were cultured on fibronectin coated, 8-well ECIS chamber slides. Basal resistance of LacZ and MEK5/CA HDMECs were measured at maximal resistance. Individual points and Mean (+/− Std Dev.) presented. B) siRNA reversal of MEK5/CA barrier reduction. MEK5/CA cells were transfected with either Control, MEK5-, or KLF4-specific siRNA. Electrical resistance was monitored until maximum resistance was achieved in the Control group. Data are from one of two independent experiments with similar results and are presented as mean +/− SD; Statistical significance was determined by ANOVA. C) LacZ and MEK5/CA HDMEC were cultured on ECIS chamber slides. Electrical resistance (Ohms), was monitored to determine point of maximal monolayer resistance. Increasing doses of TNF (0.1, 1, 10, and 100 ng/ml) were added in triplicate to culture wells and electrical resistance was measured for a period of 10 hours. Curves represent means of triplicate wells. Error bars were excluded for clarity. D) Results from (C) were used to calculate EC50. The untreated control (0 ng/ml TNF) was designated as 0% vascular leak and 100 ng/ml TNF dose as 100% leak and used to calculate a maximum change in resistance. The maximum resistance difference (RD) between 0 and 100 % vascular leak was used to calculate percentage of leak for each experimental condition: [(RD (TNF dose)/RD (maximum)*100)]. Non-linear regression curve and EC50 was calculated. The results represent the means and SEM of three independent experiments. Statistical significance was determined by paired t-test.