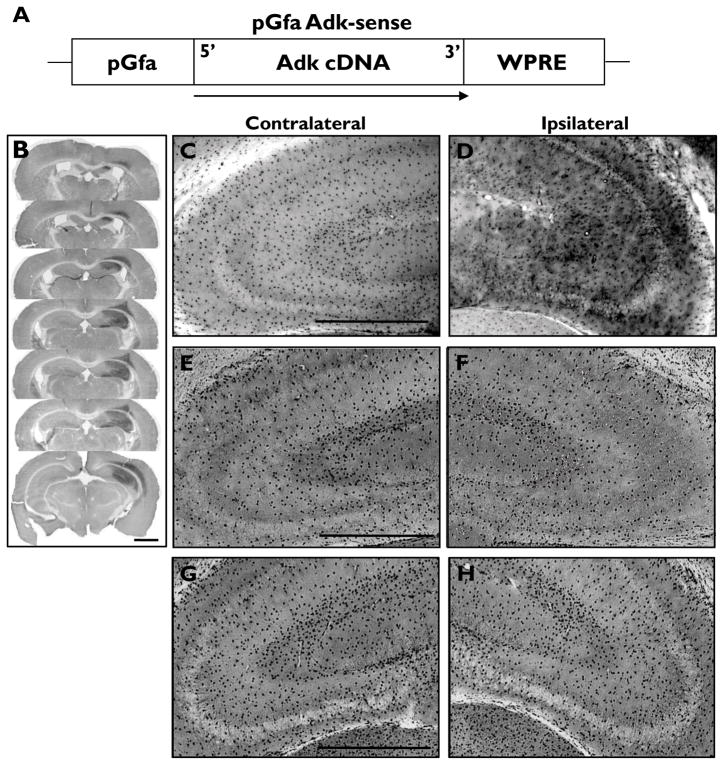
Figure 1.
Overexpression of ADK by unilateral injection of the astrocytic AAV- Adk-SS virus. (A) Schematic illustration of the pGfa-Adk-sense (Adk-SS) vector coding region. The Adk-cDNA is oriented in the sense direction (5′ to 3′) under control of the truncated astrocyte specific gfaABC1D promoter (pGfa). The transcriptional woodchuck hepatitis virus transcriptional regulatory element (WPRE) is placed downstream of the Adk-cDNA to induce expression of intronless viral messages and to increase the stability and level of gene expression. (B-H) Immunohistochemistry using ADK primary antibodies and DAB enhancement in wild-type mice injected with either Adk-SS or AAV-null and naive non-injected controls. (B) Coronal sections of wild-type mouse subjected to unilateral injection of Adk-SS virus into the CA3 region of the hippocampus illustrate the rostral to caudal and median to lateral extent of virus spread. (C, D) Higher magnification images of the contra- and ipsilateral hippocampus of Adk-SS injected wild-type mice with increased astrocytic ADK expression ipsilateral to the injection site (panel D) compared to the non-injected contralateral side (panel C). (E-H) ADK immunoreactivity in contra- (panels E, G) and ipsilateral (panels F, H) hippocampus of AAV-null (panels E, F) and saline (panels G, H) injected wild-type mice with comparable ADK expression in the contra- (panel G) and ipsilateral sides (G, H). Scale bars = 1mm B; 500 μm C-H; 300 μm.