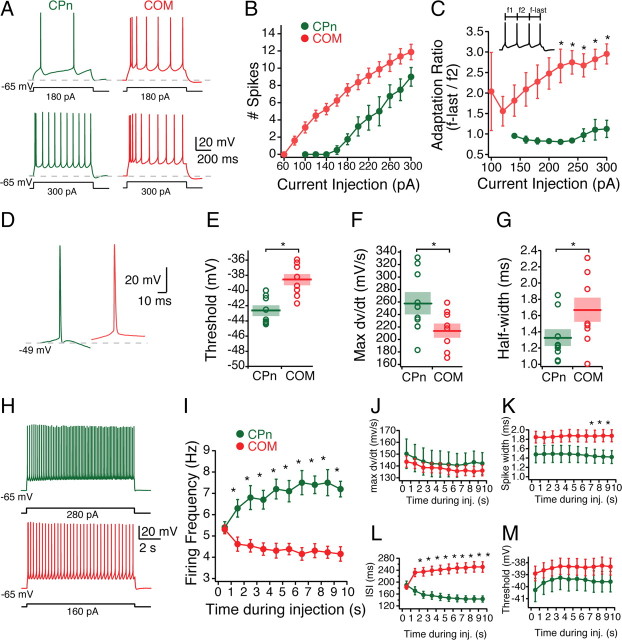
Figure 7.
Active properties of COM versus CPn neurons. A, Representative responses of COM (red) and CPn neuron responses to 750 ms step depolarizations of 180 and 300 pA. B, Firing frequency of spikes elicited across a range of current injections (60–300 pA). C, Ratio of the first ISI to the last ISI. D, Representative traces of the first action potential in COM and CPn neurons with sufficient current to trigger four action potentials in 750 ms. Action potentials in CPn neurons were typically followed by a fast afterhyperpolarization and fast ADP. E–G, Threshold, rate of rise (max dv/dt), and AP half-widths of COM and CPn neurons. H, COM neurons exhibit spike frequency adaptation, whereas CPn neurons exhibit spike acceleration. Representative traces of a 10 s current injection that elicits 5 Hz firing frequency in the first second. I–M, Changes in firing frequency, max dv/dt, interspike interval, spike width, and threshold over the course of a 10 s current injection. *p < 0.05.