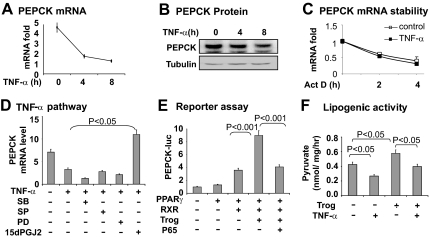
Fig. 2.
Pepck inhibition by TNF-α in adipocytes. A, Inhibition of Pepck mRNA expression by TNF-α in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. The cells were serum starved overnight and treated with TNF-α (20 ng/ml) for different times as indicated. The total RNA was extracted and subjected to qRT-PCR analysis for Pepck mRNA. B, Inhibition of PEPCK protein expression by TNF-α. The cells were serum starved overnight and treated with TNF-α (20 ng/ml). The PEPCK protein was determined in the whole-cell lysate in a Western blot with anti-PEPCK antibody. C, Influence of TNF-α on the Pepck mRNA stability. De novo mRNA expression was inhibited in 3T3-L1 adipocytes by actinomycin D (5 μg/ml). Then the cells were treated with TNF-α (20 ng/ml, filled square) for different times as indicated. The Pepck mRNA was quantified by qRT-PCR. D, TNF-α activity in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. The 3T3-L1 adipocytes were pretreated with the pharmacological inhibitors for 30 min. The inhibitors are SB203580 (SB; 10 μm), SP600125 (SP; 25 μm), PD98059 (PD; 40 μm), 15dPGJ2 (15 μm). PEPCK mRNA was determined 6 h later after addition of TNF-α. E, Blocking of PPARγ activity by p65. In this experiment, PPARγ and RXR were cotransfected with a Pepck -luciferase reporter. F, Lipogenesis for PEPCK activity in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. The pyruvate incorporation assay was performed in cells after treatment with TNF-α (20 ng/ml) or troglitazone (Trog; 10 μm) for 4 h. In this figure each bar represents mean ± sem (n = 3–8).