Fig. 1.
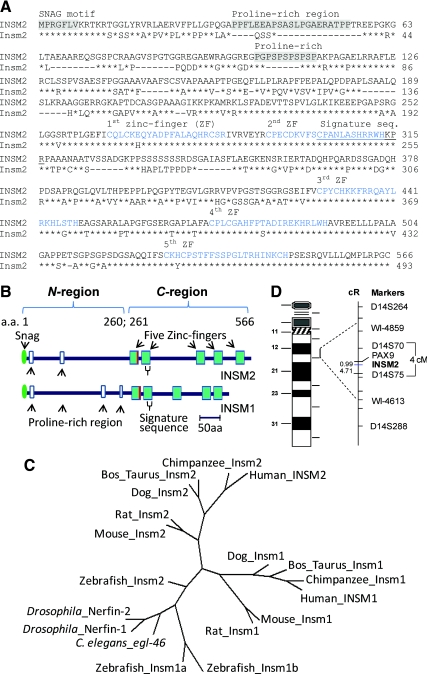
INSM2 analysis. A, Comparison of the human (upper lines) and mouse INSM2 (lower lines) shows their similarities in Snail/Gfi-1 (SNAG) motif (a.a. 1–7), two proline-rich regions (a.a. 35–55 and 102–115), and five zinc-finger motifs (a.a. 261–566). The signature sequence (a.a. 302–316) of the family is underlined. B, Schematic comparison of INSM2 structure with INSM1. The last residue of histidine of the first zinc-finger is replaced by arginine (in red). C, The phylogenetic tree was generated from multiple amino acid alignments (Supplemental Table 1, published on The Endocrine Society's Journals Online web site at http://endo.endojournals.org). D, The integrated chromosome map shows the INSM2 location between D14S70 and D14S75.