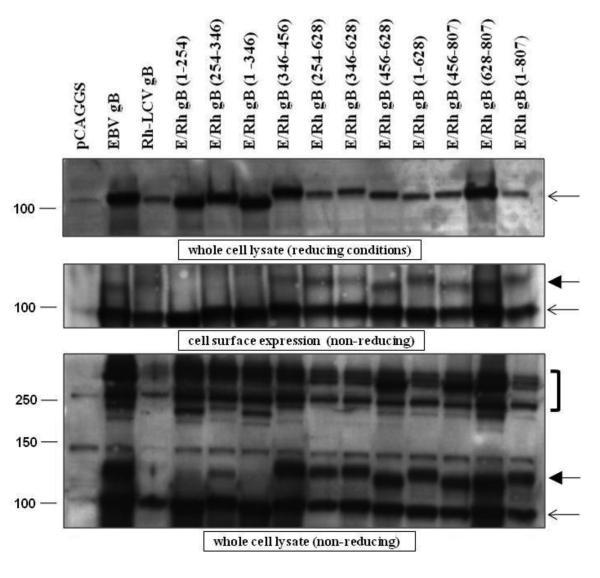
Figure 3. Expression levels of most of the EBV/Rh gB chimeras are similar to that of EBV gB.
CHO-K1 cells were transfected with EBV gB, Rh-LCV gB, and the EBV/Rh gB chimeras as described in Materials and Methods. (A) Western blot analysis of EBV/Rh gB chimera expression in whole cell lysates was determined under reducing conditions. Molecular weight marker in kDa is indicated and the open arrow indicates the position of full length EBV gB. (B) The cell surface expression of EBV/Rh gB chimeras was determined by biotinylation of cell membranes followed by immunoprecipitation with a monoclonal gB antibody. Western blot analysis of EBV/Rh gB chimeras was done under non-reducing conditions with a polyclonal gB antibody. Molecular weight marker in kDa is indicated and the open arrow indicates the position of full length EBV gB. (C) Oliogomer formation of EBV/Rh gB chimeras was examined in whole cell lysates under nonreducing conditions. Oligomers are identified by brackets to the right of the blot, monomeric gB is indicated by an open arrow, and the fully glycosylated mature form of gB indicated by a closed arrow.