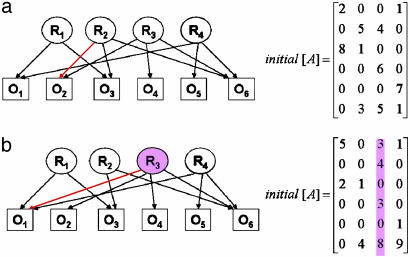
Fig. 2.
A completely identifiable network (a) and an unidentifiable network (b). Although the two initial [A] matrices describing the network matrices have an identical number of constraints (zero entries), the network in b does not satisfy the identifiability conditions because of the connectivity pattern of R3. The edges in red are the differences between the two networks.