Figure 2.
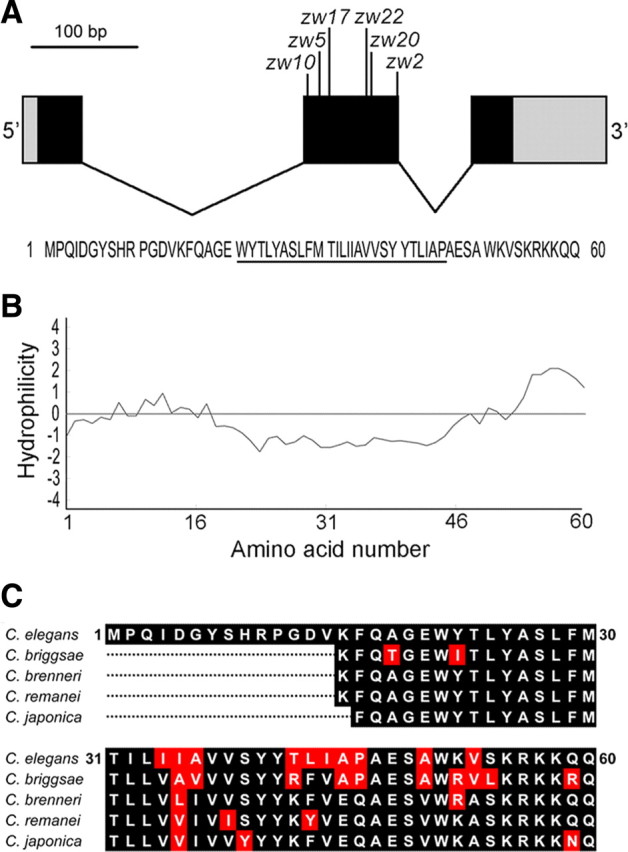
bkip-1 encodes a novel protein with homologs in nematodes. A, A diagram showing bkip-1 exon–intron organization and locations of the mutations identified in bkip-1 alleles. Coding exons are shown in black, 5′ and 3′ untranslated regions are in gray, and introns are as black lines. Molecular lesions of the six bkip-1 alleles are as follows: zw2 (P46L); zw5 (G19S), zw10 (splice acceptor site mutation leading to a frame shift after K15 and then a stop codon, LNQHGKYQSEKSSSEFASRPYK STOP); zw17 (W21 to STOP), zw20 (V37D), and zw22 (single nucleotide deletion in exon 2 leading to a frame shift after A36 and then a stop codon, QSSHIIHLLLLLNQHGKYQSEKSSSEFASRPYK STOP). Bottom, Deduced amino acid sequence of BKIP-1. The putative transmembrane domain is underlined. B, Kyte–Doolittle hydrophilicity plot of BKIP-1 showing that a stretch of hydrophobic amino acid residues that could potentially serve as a membrane-spanning domain. C, Alignment of BKIP-1 with putative homologs in several nematode species. The putative homologs were identified through blast search of the respective nematode genomes. The N-terminal portions of the putative homologs were excluded from the alignment because they cannot be readily predicted.
