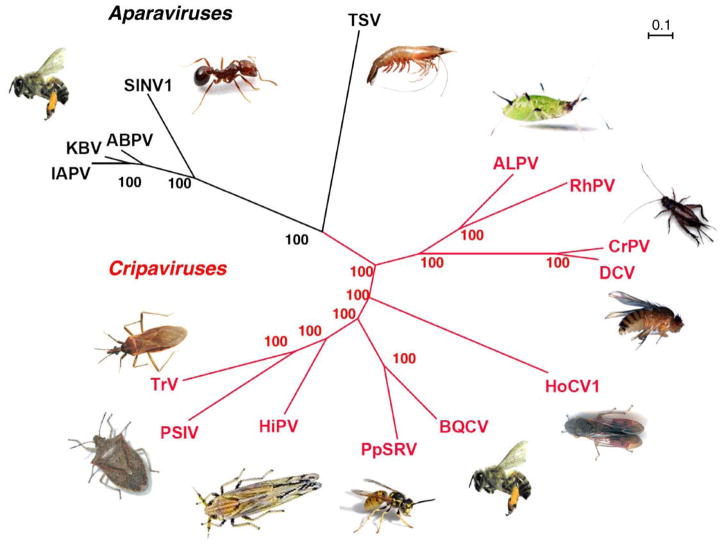
Fig. 1.
Phylogenetic tree for Dicistroviridae. The phylogenetic tree was derived from the protein sequence of the structural genes. The genera Cripavirus (red) and the Aparavirus (black) are shown with the host next to the virus. The predicted amino acid sequences were aligned using ClustalW2 (Chenna et al., 2003). Trees were predicted using MrBayes (Huelsenbeck and Ronquist, 2001) and formatted with Dendroscope (Huson et al., 2007). Bootstrap values are indicated at the nodes. The full virus names and GenBank accession numbers are as follows: IAPV = Israeli acute paralysis virus (NC009025), KBV = Kashmir bee virus (NC004807), ABPV = acute bee paralysis virus (AF150629), SINV-1 = Solenopsis invicta virus-1 (AY634314), TSV = Taura syndrome virus (AF277675), PSIV = Plautia stali intestine virus (AB006531), TrV = Triatoma virus (AF178440), HiPV = Himetobi P virus (AB017037), BQCV = black queen cell virus (AF183905), PpSRV = Pteromalus puparum small RNA virus (EU680971.1), HoCV-1 = Homalodisca coagulata virus-1 (NC008029), ALPV = aphid lethal paralysis virus (AF022937), RhPV = Rhopalosiphum padi virus (AF022937), CrPV = cricket paralysis virus (AF218039), and DCV = Drosophila C virus (AF014388).