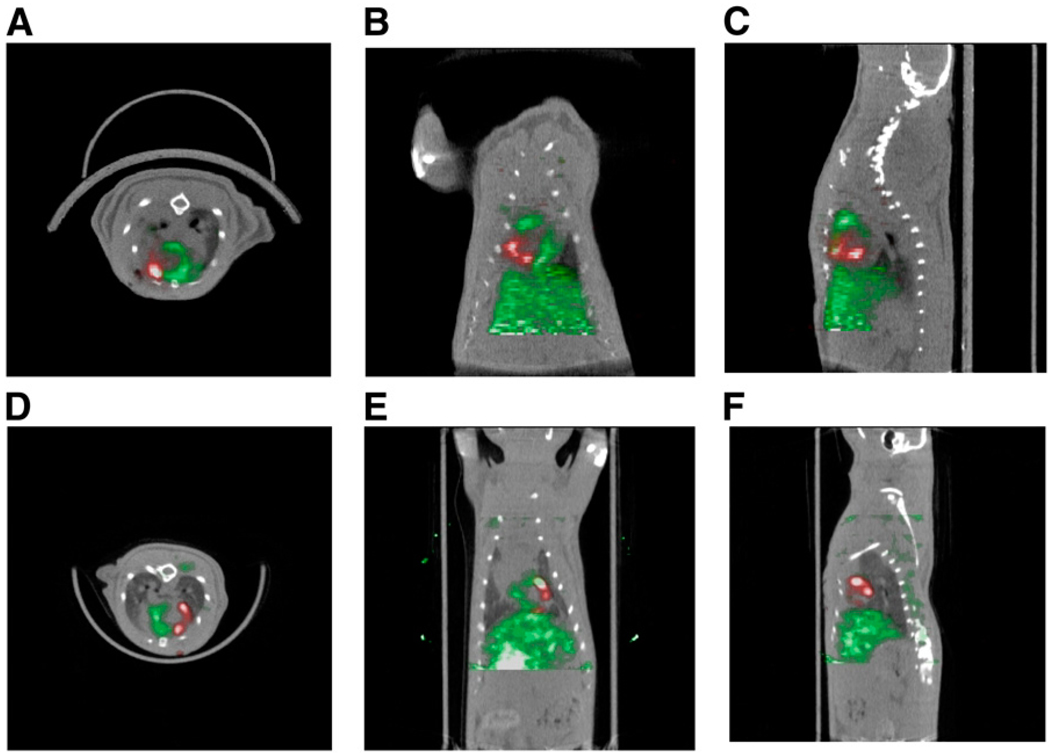
FIGURE 2.
(A–C) Detection of 18F-FDG–labeled cardiac-derived stem cells (CDCs) in rat heart by small-animal PET/CT. CDCs were labeled with 74 kBq of 18F-FDG per milliliter and injected intramyocardially after ligation of mid left anterior descending coronary artery. PET was performed immediately after cell transplantation. Myocardium (green) was delineated by intravenous injection of 37 MBq of 13N-NH3. Cells (red) were visualized within perfusion deficit by PET. Transverse (A), coronal (B), and sagittal (C) image orientations are shown. (D–F) SPECT/CT of sodium-iodide symporter-transduced CDCs in rat heart. CDCs were transduced with lentivirus expressing sodium-iodide symporter driven by constitutively active promoter, cytomegalovirus, and injected intramyocardially after ligation of mid left anterior descending coronary artery. SPECT/CT dual-isotope imaging was performed 24 h after cell transplantation. Myocardium (green) was delineated by intravenous injection of 201Tl. Transplanted cells (red) were identified within perfusion deficit by SPECT after intravenous injection of 99mTc. Transverse (D), coronal (E), and sagittal (F) image orientations are shown.