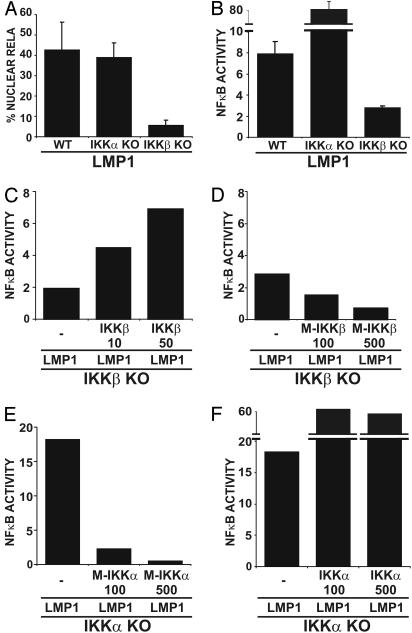
Fig. 1.
The role of IKKα and IKKβ in LMP1-mediated NF-κB activation in MEFs. (A) WT, IKKα KO, and IKKβ KO MEFs were transfected with GFP-RelA and IκBα-encoding plasmids in the presence or absence of an LMP1 expression plasmid. The percentage of cells with nuclear translocation of GFP-RelA induced by LMP1 is shown. Average values ± SD are shown from three experiments, in which LMP1 expression was similar in all transfected MEFs (not shown). (B) WT, IKKα KO, and IKKβ KO MEFs were transfected with 3XκBL and pGK-β-gal alone or with LMP1. The mean folds of NF-κB activation by LMP1 ± SE relative to β-gal activity are shown from one representative of four independent experiments performed in duplicate. (C) Folds of NF-κB activation by LMP1 alone or in the presence of increasing amounts (in ng) of WT IKKβ expression vector in IKKβ KO MEFs are shown from a representative transfection. (D) Folds of NF-κB activation by LMP1 alone or in the presence of increasing amounts (in ng) of catalytically inactive IKKβ (M-IKKβ) in IKKβ KO MEFs are shown from a representative transfection. (E) Folds of NF-κB activation by LMP1 alone or in the presence of increasing amounts (in ng) of catalytically inactive IKKα (M-IKKα) in IKKα KO MEFs. (F) Folds of NF-κB activation by LMP1 alone or in the presence of increasing amounts (in ng) of WT IKKα expression vector in IKKα KO MEFs.