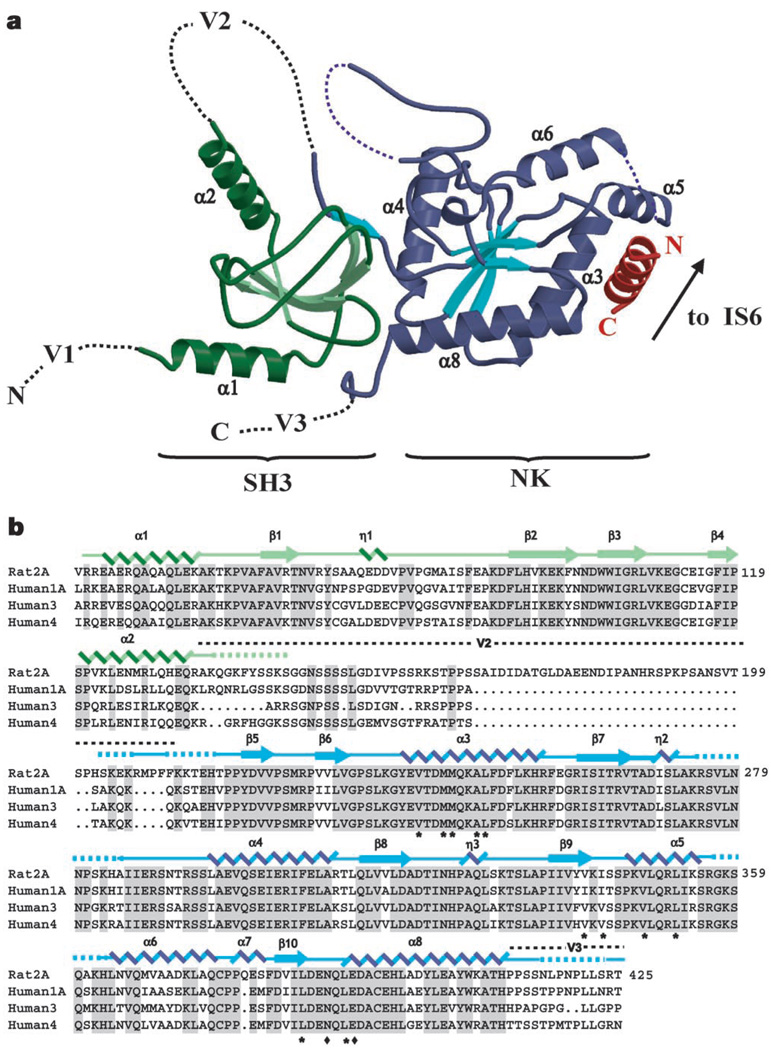
Figure 1.
Structure of the CaVβ2a–CaV1.2 AID complex. a, Ribbon diagram of the complex. Dashed lines indicate regions absent from the structures. SH3 and nucleotide kinase (NK) domains are shown in green and blue, respectively. The AID is shown in red. CaVβ2a α-helices are labelled. Variable regions V1, V2 and V3 are indicated. The CaVβ2a unbound structure is similar to that shown here for the complex. The arrow indicates where the AID connects to transmembrane segment IS6. b, Sequence alignment of representatives of each CaVβ isoform. The top sequence shows residues 40–425 of rat Cavβ2a. Numbers on the right denote each line’s terminal residue. Shading denotes residues identical among isoforms. The two Cavβ2a domains used for crystallization are indicated in green and blue, respectively. Secondary structure elements are indicated: α, α-helix; η, 310 helix; β, β-strand. Dashed lines indicate residues present in the crystallized constructs but absent in the electron density. Location of the V2 and part of the V3 regions are shown. Asterisks identify residues that contribute side-chain contacts to the AID-binding pocket; diamonds mark side chains with direct hydrogen bonds to the AID.