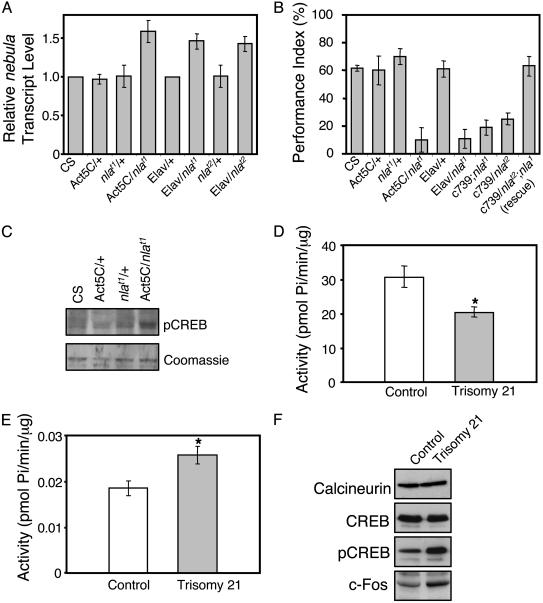
Fig. 3.
Transgenic flies overexpressing nebula show defective learning, and human trisomy 21 fetal brain tissues overexpressing DSCR1 exhibit altered calcineurin-mediated signaling. (A) Quantitative real-time RT-PCR results. n = 3 independent experiments done in triplicate. Note that nlat1 and nlat2 transgenic flies show the same level of nebula overexpression in the presence of Elav-GAL4 driver. (B) Performance index values for Pavlovian olfactory learning. Flies overexpressing nebula by using the Act5C driver (Act5c/nlat1), Elav driver (Elav/nlat1), and mushroom bodies-specific driver (c739/nlat1 and c739/nlat2) show severely impaired learning. Overexpression of nebula in the mushroom bodies of the homozygous nebula loss-of-function mutant (c739/nlat2;nla1) shows complete rescue of the learning defect. (C) Western blot analysis shows that the level of pCREB in Act5C/nlat1 is higher than that of the control lines (CS, Act5C/+, nlat1/+). Coomassie staining confirms the amount loaded. (D) Calcineurin activity in control and trisomy 21 fetal brain tissues. (E) PKA activity in control and trisomy 21 fetal brain tissues. (F) Western blots showing calcineurin, CREB, pCREB, and c-Fos protein levels in control and trisomy 21 fetal brain tissues. All values represent mean ± SEM. For A, n = 4 experiments done in triplicate. n = 4 for each fly strain in B. For D and E, n = 3 experiments done in triplicate.*, P < 0.05 as determined by Student's t test.