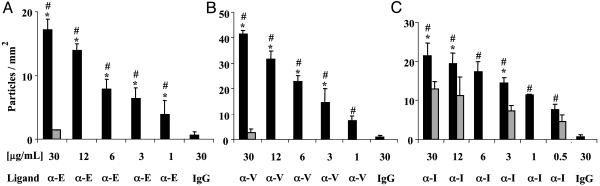
Fig. 2.
LEAPs exhibit selective adhesion to cytokine activated HUVEC. Separate sets of PLA–PEG particles, conjugated with a mAb to an ECAM or mouse IgG (negative control), were perfused over HUVEC in an in vitro flow chamber. The number of LEAPs adherent to the HUVEC was determined after 2.5 min of flow. Black bars indicate adhesion to 4 h cytokine (IL-1β in A and C or TNF-α in B) activated HUVEC. Gray bars indicate adhesion to unactivated HUVEC; μg/ml is the concentration of ligand (either a mAb or mouse IgG) used during the conjugation procedure. Ligand indicates which molecule was coupled to the PLA–PEG particles, a mAb to E-selectin (α-E), VCAM-1 (α-V), ICAM-1 (α-I), or mouse IgG (IgG). Shear stress = 1.5 dynes/cm2; n ≥ 3; ANOVA indicated that the level of adhesion of the LEAPs to cytokine activated HUVEC was a function of the concentration of mAb used in the coupling procedure. *, P < 0.05 compared to LEAPs over unactivated HUVEC (gray bars); #, P < 0.05 compared to 30 μg/ml mouse IgG PLA–PEG particles over 4 h IL-1β or TNF-α-activated HUVEC.