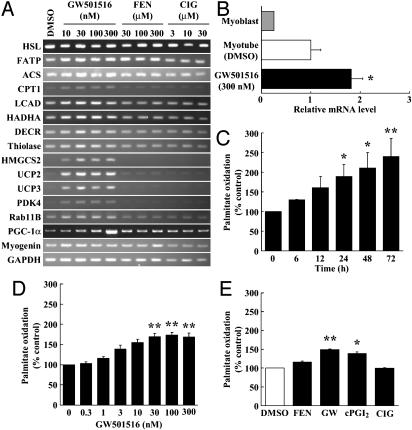
Fig. 1.
PPARδ agonists increase fatty acid oxidation in L6 myotubes. (A) RT-PCR analyses of PPARδ-regulated genes in L6 myotubes. (B) Real-time PCR analysis of PGC-1α mRNA levels in L6 myoblast/myotube cells exposed to GW501516. (C) Time responses on fatty acid oxidation in L6 myotubes exposed to GW501516. Cells were cultured with 100 nM GW501516 at the indicated times. (D) Dose responses on fatty acid oxidation in L6 myotubes exposed to GW501516. L6 myotubes were cultured with the indicated concentrations of GW501516 for 24 h. (E) The effect of the PPAR agonists on [14C]palmitate oxidation. After incubation in differentiation medium for 7 days, L6 myotubes were treated with DMSO (control), FEN (300 μM), GW501516 (100 nM), cPGI2 (10 μM), or CIG (30 μM) for 24 h. All assays were performed in triplicate, and each bar represents the mean ± SE of three to four independent experiments. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01 compared with vehicle-treated control. HADHA, mitochondrial trifunctional protein; DECR, mitochondrial 2,4-dienoyl CoA reductase 1; HSL, hormone-sensitive lipase.