Figure 2. Genomic classical and non-classical actions of ER.
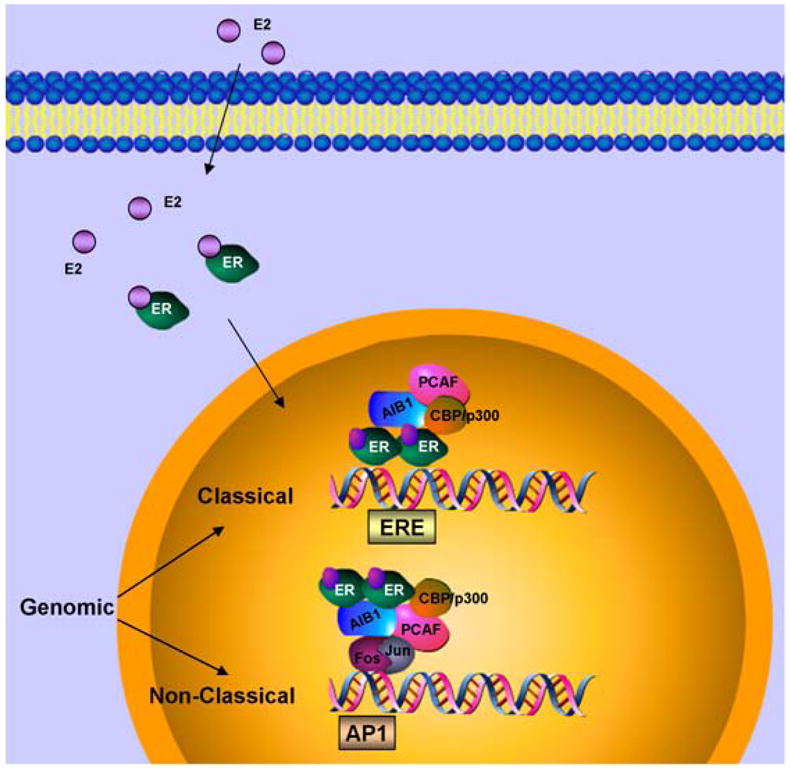
In classical genomic mode of action, estrogen (E2) binds estrogen receptor (ER), induces dimerization of the receptors, nuclear translocation and recruitment to estrogen response element (ERE) in the promoter region of the target genes. Coactivators such as AIB1, CBP/p300, PCAF are recruited to the transcription complex followed by gene transcription. In non-classical mode of action, estrogen bound ER gets recruited to other transcription factors such as Jun/Fos to activate transcription.
