Fig. 1.
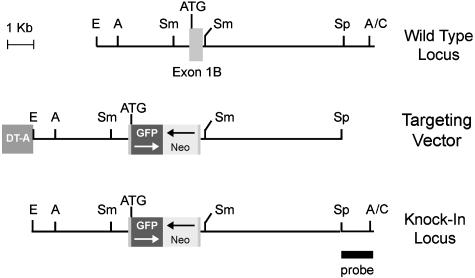
Targeting of the Arf locus surrounding exon 1β. A schematic map of the region flanking exon 1β (Top), relevant sequences in the targeting vector (Middle), and the knock-in allele (Bottom) are illustrated. Arf coding sequences were replaced by a cassette encoding enhanced GFP and the neomycin-resistance gene (neo) in opposite orientations (arrows). The neo gene includes its own 5′ promoter, whereas GFP expression is driven by the Arf promoter; both neo and GFP terminate with 3′ polyadenylation signals. The targeting vector contains a gene encoding the diphtheria toxin A chain (DT-A), which is toxic unless eliminated and therefore selects against nonhomologous recombination of the targeting vector elsewhere in the mouse genome. The probe used to score the different alleles is illustrated at the bottom right. ATG refers to the position of the GFP initiation codon. Restriction sites for EcoR1 (E), AflII (A), SmaI (Sm), SpeI (Sp), and ClaI (C) are indicated.