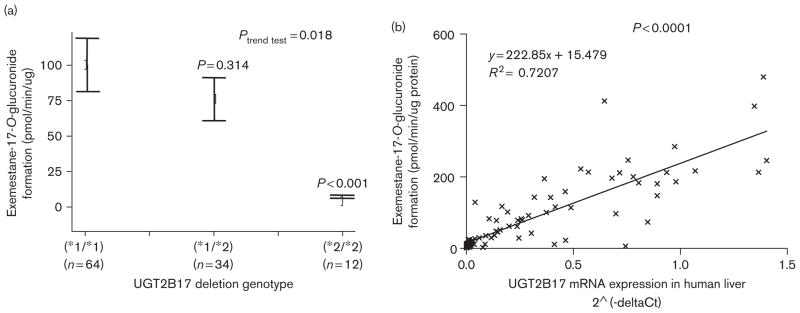
Fig. 5.
Human liver microsome (HLM) glucuronidating activity against 17-dihydroexemestane versus UGT2B17 genotype and UGT2B17 mRNA expression in human liver. Panel (a), exemestane-17-O-glucuronide formation versus UGT2B17 genotype in HLM. Glucuronidation activity assays were performed using 9.4 μmol/l 17-dihydroexemestane and the glucuronide of 17-dihydroexemestane was separated by UPLC as described in the Materials and methods section. Real-time PCR was performed using genomic DNA from the same liver specimens for which HLMs were also prepared and used to determine UGT2B17 (*1/*1), (*1/*2), and (*2/*2) genotypes. Comparative analysis was performed using HLM from individuals with the UGT2B17 (*1/*1) genotype as the reference, with the P value shown for HLM from individuals with the UGT2B17 (*1/*2), (*2/*2) genotype. Panel (b), exemestane-17-O-glucuronide formation versus UGT2B17 mRNA expression in human liver. UGT2B17 mRNA expression was determined relative to PPIA as the housekeeping gene by real-time PCR by our group previously as described in the Materials and methods section.