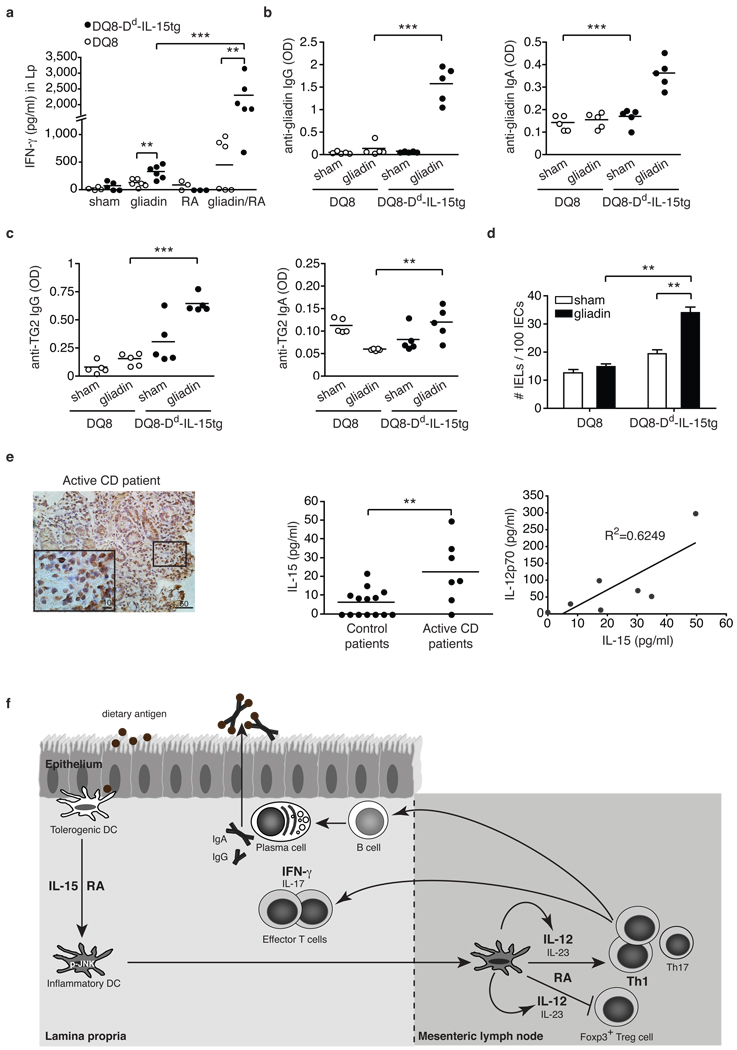
Figure 4. DQ8-Dd-IL-15tg mice fed gliadin mimic early stages of celiac disease reflecting dysregulation in the adaptive immune response to gluten.
a-d, DQ8 and DQ8-Dd-IL-15tg mice were fed gliadin every other day for ten days. a, IFN-γ secretion by Lp cells after overnight culture with gliadin. b, c, Anti-gliadin IgG, anti-gliadin IgA, anti-TG2 IgG and anti-TG2 IgA titers from serum collected fifteen days after feeding. d, Quantification of IEL among intraepithelial cells in small intestines fifteen days after the last feeding. e, IL-15 and IL-12 expression in the Lp of CD patients. Immunohistochemical stainings for IL-15 in gut tissue from an active celiac disease patient (left panel). Lp cells were harvested from biopsies obtained from control (n=14) or active CD patients (n=7) and assayed for levels of IL-15 and IL-12p70 by ELISA (middle and right panels). Equal concentration of total proteins was analyzed for each sample. **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 (unpaired Student's t-test). f, Proposed model for the co-adjuvant effects of RA and IL-15 in the intestinal mucosa. Under inflammatory conditions, the expression of the pro-inflammatory cytokine IL-15 is upregulated in the Lp of the small intestine. Through the synergistic action of IL-15 and RA, DC acquire the ability to release inflammatory cytokines, particularly IL-12 and IL-23. These inflammatory mediators then act in concert with RA to prevent the induction of Foxp3+ Treg cells and drive TH1 and potentially TH17 polarization. In turn, inflammatory T cells may provide help to B cells to produce specific IgG and IgA antibodies.