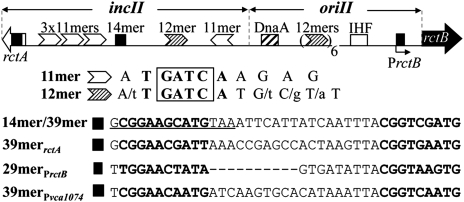
Fig. 1.
A map of V. cholerae chrII region relevant to replication initiation. Also shown are sequences that bind RctB. Two genes, rctB (black arrow) and rctA (white arrow), flank the region. rctB encodes the chrII-specific replication initiator RctB, whereas rctA is transcribed only. PrctB and PrctA are promoters, both regulated by RctB (9, 11). oriII is the minimal region capable of autonomous replication in the presence of RctB in E. coli. incII controls oriII activity. Other than the binding sequences for DnaA and IHF, the rest of the elements are binding sites for RctB. The white and shaded arrowheads represent the iterons (11- and 12-mers with a guanine/adenine/thymine/cytosine (GATC) sequence). The black square in the middle of incII, originally called a 14-mer (the underlined sequence), is found here to be a part of a 39-mer, which can bind RctB; it consists of two direct repeats (shown in bold letters), linked by an AT-rich region. Also shown are three other 39-mer–like sites present in chrII, although in one case the AT-rich region was 9-bp, instead of 19-bp, long (29-merPrctB).