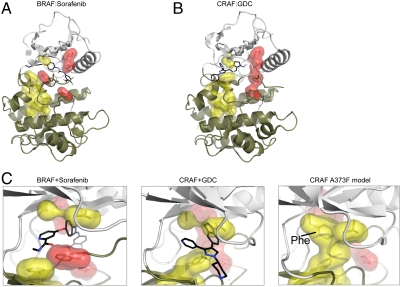
Fig. 3.
Modeling the structural effects of the alanine to phenylalanine change in CRAF and BRAF. The position of residues constituting the hydrophobic spines of CRAF crystallized with a type I inhibitor (stabilizes the closed and ATP bound form of the kinase) are shown in B, and the hydrophobic spine residues in BRAF bound to a type II inhibitor (binds to the open conformation preventing closing of the cleft) is shown in A. Components of the catalytic hydrophobic spine are shown in yellow, whereas components of the regulatory hydrophobic spine are shown in red. Note the contiguous residues of red and yellow induced by the type I inhibitor in B, whereas the pattern of these residues is interrupted in A. Note also how the drug molecule in B functions to connect components of the catalytic hydrophobic spine in the upper and lower lobes of the kinase. In C, a simulated structure of CRAF where A373 is replaced with Phe is shown (Right). Energy minimization was done using the program TINKER. The minimized structure is rotated 90° in D to show more clearly how the C spine is stabilized and completed by the Phe mutation. For each structure, the N lobe is shown in white and the C lobe in tan.