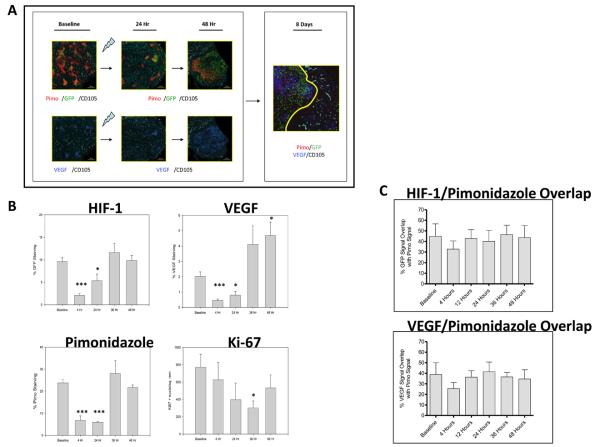
Figure 3.
Post-radiation in vivo HIF-1 signal induction results from stromal vessel dysfunction and ischemic insult. A) Serial 4X photomicrographs of immunohistochemical staining for HIF-1, pimonidazole, VEGF, and CD105+ microvessels in control and irradiated #4C6 xenograft tumors. Images from 24 hours post-treatment tissue samples illustrate focal radioresistant HIF-1 dependent GFP signal and VEGF expression in regions retaining pimonidazole 24 hours post-treatment. By 8 days post-treatment, normalization of HIF-1 transcriptional activity, VEGF expression, and pimonidazole staining is seen in revascularized regions populated with CD105+ vessels. However, tumor adaptation is not uniform; areas of pimonidazole retention, HIF-1 dependent GFP signal, and VEGF protein co-localize to focal devascularized regions (to the left of the revascularized region demarcated by the solid yellow line), recapitulating the heterogeneous tumor microenvironment seen at baseline. B) Quantification of % staining of total tissue area over time in pooled tissue sections, reported as mean values +/− s.d. All statistical comparisons are with baseline pretreatment values; *, p < 0.05; ***, p < 0.001. C) Quantified pixel-by-pixel analysis of % spatial overlap +/− s.d. between GFP/VEGF signal and pimonidazole, at baseline and following irradiation.