Figure 5.
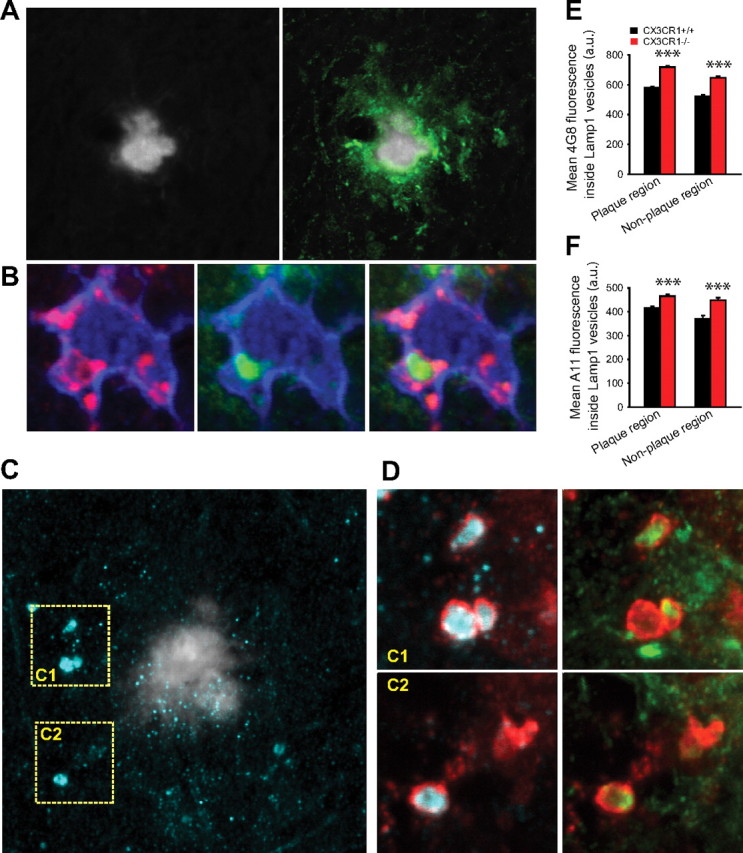
CX3CR1-deficient microglia have an enhanced capacity for protofibrillar Aβ phagocytosis in vivo. A, Confocal image shows a thioflavin-S fibrillar plaque (gray) surrounded by a large halo of 4G8-immunoreactive protofibrillar Aβ (green). B, High-resolution confocal image of a plaque-associated IBA1-labeled microglia (blue) containing a 4G8-immunoreactive Aβ aggregate (green) within a LAMP1-immunoreactive phagolysosome (red). C, Left panel, Thioflavin-S-labeled fibrillar plaque (gray) surrounded by abundant A11-immunoreactive oligomeric Aβ (cyan). D, Insets C1 and C2 correspond to dotted squares in Figure 4C. Large LAMP1-labeled phagolysosomes (red) (which are exclusively present in microglia) (supplemental Fig. 2, available at www.jneurosci.org as supplemental material) contain abundant A11-immunoreactive oligomeric (cyan) and 4G8-immunoreactive protofibrillar Aβ. E, F, Quantification of 4G8 and A11 fluorescence inside LAMP1-immunoreactive phagolysosomes near (<25 μm) and away from fibrillar plaques. Microglial phagolysosomes in CRND8/CX3CR1−/− mice exhibit a significant increase in 4G8 and A11 content in both plaque and nonplaque regions compared with CRND8/CX3CR1+/+ mice (***p < 0.001; values are expressed as mean ± SEM; n = 3 mice, 180 plaques, and >4000 lysosomes per genotype).
