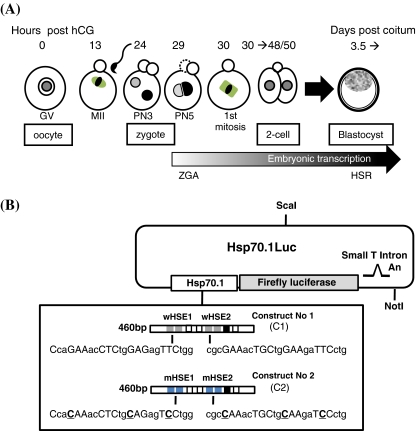
Fig. 1.
Biological and molecular materials used to study Hsp70.1 expression in oocytes and preimplantation embryos. a Description of the oocyte and embryonic developmental stages. Fully grown ovarian oocytes are noted germinal vesicle (GV) oocytes from the name given to their voluminous nucleus. Around ovulation, GV oocytes resume meiosis and progress until the metaphase stage of the 2nd meiotic division (MII) awaiting fertilization. The zygote is produced by the fusion between MII oocyte and spermatozoon. The zygotic genome activation (ZGA) is initiated during the G2 phase of the first cell cycle and transcriptional activity is first observed at the level of the paternal genome (male pronucleus) (Bouniol-Baly et al. 1997; Christians et al. 1995). The first mitosis gives an embryo with two cells (two-cell stage) which cleaves about four times before the formation of the blastocyst (3.5 days post-coitum) which are able to elicit the classical heat shock response (HSR). The timing of oocyte and early embryonic development is counted as hours post-hCG (for additional description of mouse oocyte and embryo development, see Kubiak et al. 2008). b Constructs used in transgenic experiments. Constructs No. 1 (C1) and No. 2 (C2) were linearized and microinjected to generate several independent transgenic lines (see also Wirth et al. 2002: line C1.101)