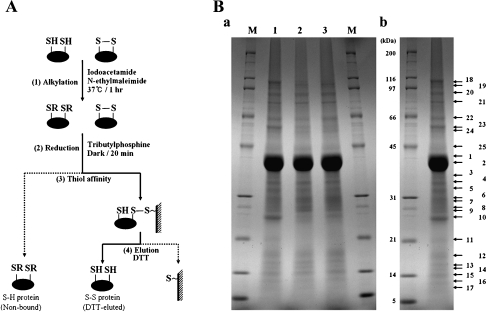
Fig. 1.
Isolation of disulfide proteins from P. putida KT2440. A Schematic drawing of the process used to isolate disulfide proteins. (1) Proteins extracted with SDS/Tris were treated with both iodoacetamide and N-ethylmaleimide to alkylate free sulfhydryls, and are designated by “R”. (2) Disulfide bonds were converted into free thiols by reduction. (3) Proteins containing thiol groups were captured by thiol-disulfide exchange between the free thiol of the protein and the resin. (4) Proteins captured on the affinity resin were eluted with dithiothreitol (DTT). B SDS-PAGE analysis of fractions from the isolation procedure. DTT-eluted proteins were separated in a 15-cm gel with a 7.5–17.5% acrylamide gradient and stained with Coomassie Brilliant Blue R-250 Ba. The same amount of eluate from each sample was loaded. Lane 1 proteins eluted from unstressed cells after recovery conditions; line 2 proteins eluted after recovery from treatment with 0.5 mM H2O2; lane 3 proteins eluted after recovery from treatment with 30 Gy gamma rays. BbNumbers indicate the protein bands analyzed by LC/MS/MS