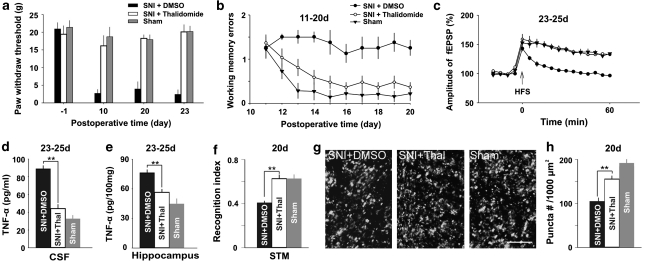
Figure 6.
Inhibition of TNF-α synthesis by thalidomide prevents memory deficits and synaptic dysfunction produced by SNI. (a) Paw withdrawal thresholds decreased in DMSO-treated SNI group but not in thalidomide-treated SNI group and sham group (n=8–10 in each group). (b) Average working memory errors in the thalidomide-treated SNI rats were lower than those in DMSO-treated SNI rats, and were not different from those in sham rats. (c) HFS induced LTP in thalidomide-treated SNI rats and sham rats but not in DMSO-treated SNI rats. (d and e) The concentration of TNF-α in three groups of rats as indicated are shown. (f) The recognition index for short-term memory was significantly higher in thalidomide-treated SNI rats than that in DMSO-treated SNI rats. There is no difference between sham rats and thalidomide-treated SNI rats (n=8 in each group). (g and h) The density of presynaptic terminal puncta was higher in thalidomide-treated SNI group than that in DMSO-treated SNI group (n=8 in each group). Scale bar=10 μm. **P<0.01 compared with DMSO-treated SNI group. Data are presented as means±SEM.