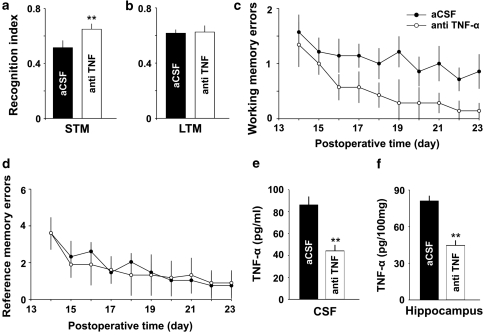
Figure 7.
Intracerebroventricular injection of TNF-α antibody attenuates memory impairment induced by SNI. (a and b) The recognition index for short-term memory but not that for long-term memory tested at 10 days and at 11 days after SNI was significantly higher in anti-TNF-α-treated group than that in aCSF-treated group (n=7 in each group). (c and d) Average working memory errors but not average reference memory errors accessed after SNI were significantly lower in anti-TNF-α-treated group, compared with aCSF-treated group (n=7 in each group). (e and f) The concentrations of TNF-α in both CSF and in hippocampus were significantly lower in anti-TNF-α-treated rats, compared with aCSF-treated rats (n=4 in each group). **P<0.01 vs aCSF-treated group. Data are presented as means±SEM.