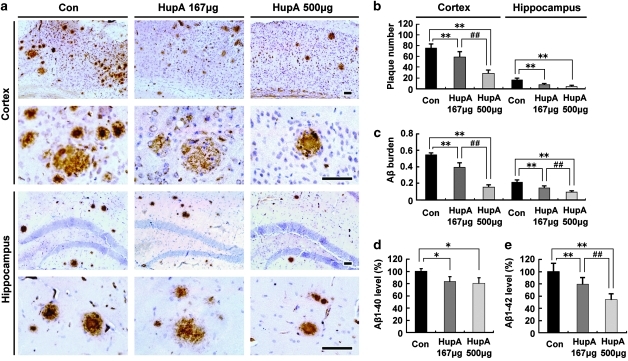
Figure 3.
Nasal gel HupA treatment significantly reduces Aβ plaque formation and soluble Aβ production in APP/PS1 mouse brain. (a) Aβ immunoreactive neuritic plaques in the cortex and hippocampus of transgenic mice treated with nasal gel and nasal gel HupA at a dose of 167 and 500 μg/kg, respectively. The number of Aβ-positive plaques was significantly reduced in HupA-treated mice compared with controls. Scale bar=60 μm. (b, c) Quantification of the number of Aβ-positive plaques (b) and Aβ burden (c) in the cortex and hippocampus of APP/PS1 mice treated with HupA. HupA significantly reduced the plaque number and Aβ burden in the brain in a dose-dependent manner. (d, e) ELISA results showed that administration of nasal gel HupA induced a dose-dependent decrease in soluble Aβ production in the cortex of APP/PS1 mice. All values are mean±SEM (n=6). *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ##p<0.01.