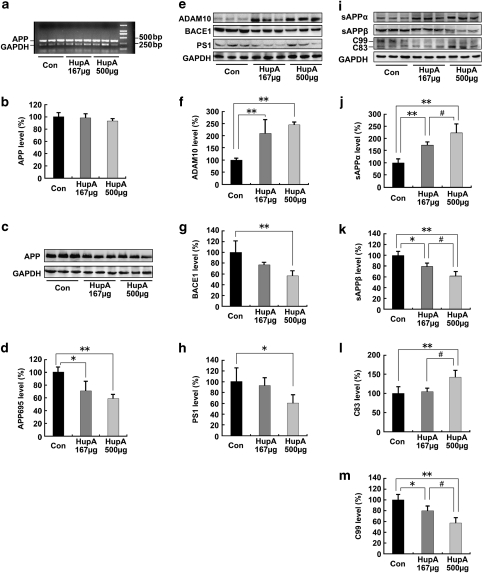
Figure 4.
Nasal gel HupA enhances the nonamyloidogenic pathway in APP/PS1 mouse brain. (a) Expression levels of APP mRNA were detected by RT-PCR in the brain of APP/PS1 transgenic mice treated with nasal gel and nasal gel HupA at a dose of 167 and 500 μg/kg, respectively. GAPDH was used as an internal reference gene. (b) HupA-treated and vehicle control APP/PS1 mice exhibited a similar APP mRNA level. (c) Western blots showed the expression levels of APP695 protein in the vehicle- and HupA-treated transgenic mouse brain. GAPDH was used as an internal control. (d) The protein levels of APP695 were significantly reduced in the nasal gel HupA-treated mouse brain compared with the vehicle controls. (e) The expression levels of APP cleavage enzymes, including ADAM10, BACE1, and PS1, were examined by western blot analysis. (f–h) Analysis results showed that the protein levels of ADAM10 were significantly increased (f), whereas the levels of BACE1 were markedly reduced in the brain of nasal gel HupA-treated mice (g). HupA treatment reduced the expression levels of PS1 protein in a dose-dependent manner, compared with vehicle controls (h). (i) Immunoblotting showed the expression levels of APP cleavage fragments, including sAPPα, sAPPβ, C83, and C99, in the vehicle- and HupA-treated transgenic mouse brain. (j–m) Quantification of sAPPα, sAPPβ, C83, and C99 generation in the brain of the APP/PS1 mouse. Nasal gel HupA treatment significantly increased the levels of sAPPα (j) and C83 (l) and reduced the levels of sAPPβ (k) and C99 (m) in a dose-dependent manner. All values are mean±SEM (n=6). *p<0.05, **p<0.01, #p<0.05.