Abstract
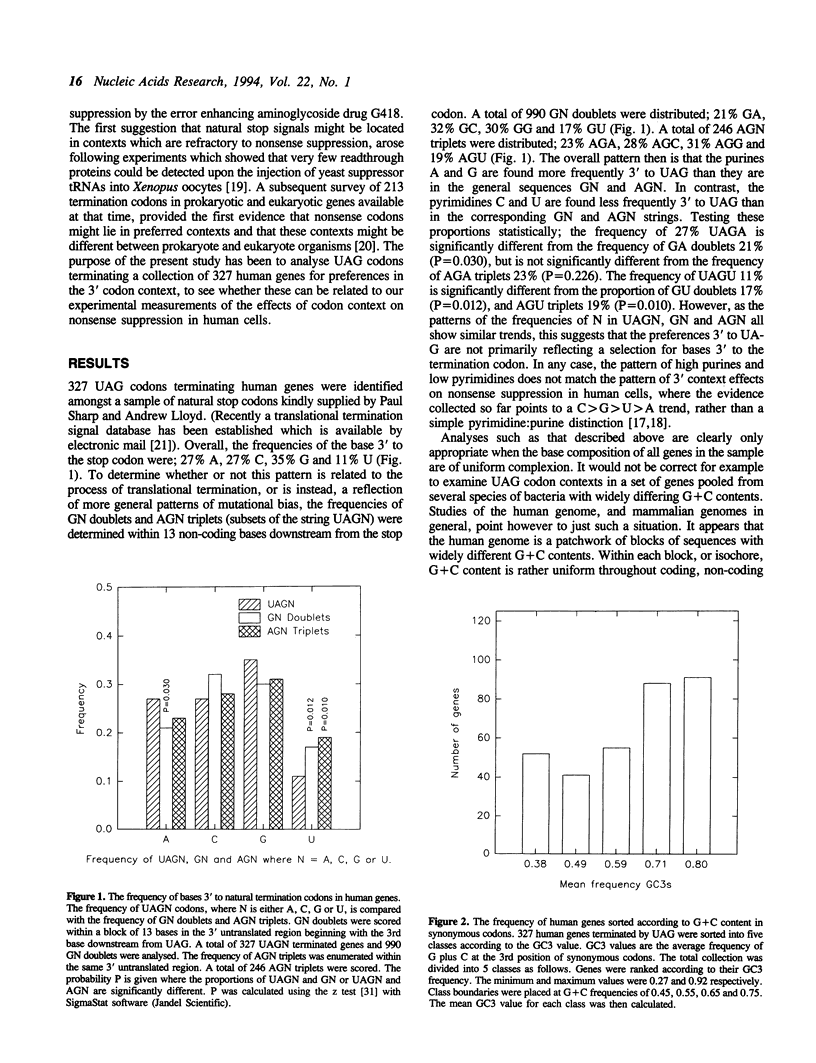
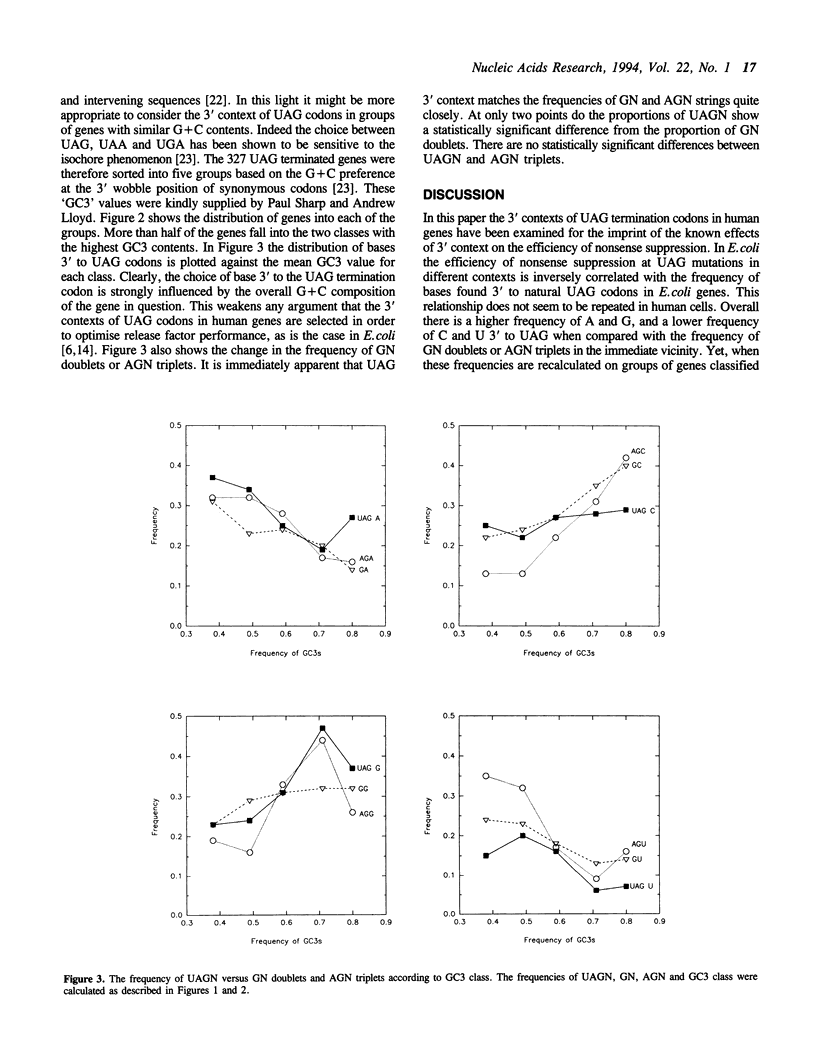
The nucleotide sequences 3' to the translational termination codons in a collection of human genes have been analysed for evidence of a preferred 3' context for natural UAG codons. The aim was to see whether human UAG contexts can be related to the recent demonstration of the effects of 3' context on nonsense suppression in human cells. Since mammalian genomes are known to consist of a patchwork of blocks of sequences or 'isochores' with different G+C contents, the collection of genes was split into 5 classes containing genes with similar frequencies of G+C at the 3rd position of synonymous codons. This analysis revealed that the frequency of bases 3' to UAG varies with the G+C frequency of the gene, and that these changes were mirrored by changes in the patterns of bases in GN and AGN strings. The identity of the next 3' base appears therefore to be determined by genome wide changes in G+C composition, rather than selection to maintain a particular tetranucleotide stop signal. These findings argue strongly that the failure to find bias in the patterns of bases used in human coding sequences is an insensitive guide for the existence of codon usage or codon context effects during translation in human cells.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersson S. G., Kurland C. G. Codon preferences in free-living microorganisms. Microbiol Rev. 1990 Jun;54(2):198–210. doi: 10.1128/mr.54.2.198-210.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angenon G., Van Montagu M., Depicker A. Analysis of the stop codon context in plant nuclear genes. FEBS Lett. 1990 Oct 1;271(1-2):144–146. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80392-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernardi G. The vertebrate genome: isochores and evolution. Mol Biol Evol. 1993 Jan;10(1):186–204. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a039994. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bienz M., Kubli E., Kohli J., deHenau S., Huez G., Marbaix G., Grosjean H. Usage of the three termination codons in a single eukaryotic cell, the Xenopus laevis oocyte. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Aug 11;9(15):3835–3850. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.15.3835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown C. M., Dalphin M. E., Stockwell P. A., Tate W. P. The translational termination signal database. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Jul 1;21(13):3119–3123. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.13.3119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown C. M., Stockwell P. A., Trotman C. N., Tate W. P. Sequence analysis suggests that tetra-nucleotides signal the termination of protein synthesis in eukaryotes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Nov 11;18(21):6339–6345. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.21.6339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown C. M., Stockwell P. A., Trotman C. N., Tate W. P. The signal for the termination of protein synthesis in procaryotes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Apr 25;18(8):2079–2086. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.8.2079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavener D. R., Ray S. C. Eukaryotic start and stop translation sites. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jun 25;19(12):3185–3192. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.12.3185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eyre-Walker A. C. An analysis of codon usage in mammals: selection or mutation bias? J Mol Evol. 1991 Nov;33(5):442–449. doi: 10.1007/BF02103136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorini L. Informational suppression. Annu Rev Genet. 1970;4:107–134. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.04.120170.000543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutman G. A., Hatfield G. W. Nonrandom utilization of codon pairs in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(10):3699–3703. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.10.3699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohli J., Grosjean H. Usage of the three termination codons: compilation and analysis of the known eukaryotic and prokaryotic translation termination sequences. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;182(3):430–439. doi: 10.1007/BF00293932. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kopelowitz J., Hampe C., Goldman R., Reches M., Engelberg-Kulka H. Influence of codon context on UGA suppression and readthrough. J Mol Biol. 1992 May 20;225(2):261–269. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90920-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li G., Rice C. M. The signal for translational readthrough of a UGA codon in Sindbis virus RNA involves a single cytidine residue immediately downstream of the termination codon. J Virol. 1993 Aug;67(8):5062–5067. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.8.5062-5067.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin R., Hearn M., Jenny P., Gallant J. Release factor competition is equivalent at strong and weakly suppressed nonsense codons. Mol Gen Genet. 1988 Jul;213(1):144–149. doi: 10.1007/BF00333411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin R., Mogg A. E., Heywood L. A., Nitschke L., Burke J. F. Aminoglycoside suppression at UAG, UAA and UGA codons in Escherichia coli and human tissue culture cells. Mol Gen Genet. 1989 Jun;217(2-3):411–418. doi: 10.1007/BF02464911. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin R., Phillips-Jones M. K., Watson F. J., Hill L. S. Codon context effects on nonsense suppression in human cells. Biochem Soc Trans. 1993 Nov;21(4):846–851. doi: 10.1042/bst0210846. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. H., Albertini A. M. Effects of surrounding sequence on the suppression of nonsense codons. J Mol Biol. 1983 Feb 15;164(1):59–71. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(83)90087-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura T., Suyama A., Wada A. Two types of linkage between codon usage and gene-expression levels. FEBS Lett. 1991 Sep 2;289(1):123–125. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80923-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen W. T., Curran J. F. Effects of the nucleotide 3' to an amber codon on ribosomal selection rates of suppressor tRNA and release factor-1. J Mol Biol. 1991 May 20;219(2):231–241. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90564-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips-Jones M. K., Watson F. J., Martin R. The 3' codon context effect on UAG suppressor tRNA is different in Escherichia coli and human cells. J Mol Biol. 1993 Sep 5;233(1):1–6. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salser W. The influence of the reading context upon the suppression of nonsense codons. Mol Gen Genet. 1969 Oct 13;105(2):125–130. doi: 10.1007/BF00445682. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp P. M., Bulmer M. Selective differences among translation termination codons. Gene. 1988;63(1):141–145. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90553-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp P. M., Stenico M., Peden J. F., Lloyd A. T. Codon usage: mutational bias, translational selection, or both? Biochem Soc Trans. 1993 Nov;21(4):835–841. doi: 10.1042/bst0210835. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tate W. P., Brown C. M. Translational termination: "stop" for protein synthesis or "pause" for regulation of gene expression. Biochemistry. 1992 Mar 10;31(9):2443–2450. doi: 10.1021/bi00124a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wada K., Wada Y., Ishibashi F., Gojobori T., Ikemura T. Codon usage tabulated from the GenBank genetic sequence data. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 May 11;20 (Suppl):2111–2118. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.suppl.2111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


