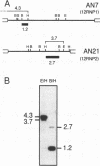
Abstract
A group of proteins containing a conserved ribonucleoprotein consensus sequence (RNP-CS)-type RNA-binding domain (CS-RBD) of approximately 80 amino acids is present in eukaryotic cells and binds specifically to a wide variety of RNA molecules. We have isolated 12 kDa single-stranded DNA binding proteins from the unicellular cyanobacterium Synechococcus 6301. The amino-terminal sequence was determined and two distinct genomic clones were isolated from a Synechococcus 6301 genomic library. Sequence analysis revealed that two closely related proteins contain a single CS-RBD of 82 amino acids and are named as 12RNP1 and 12RNP2. Both of the CS-RBDs share the highest amino acid identity with those of chloroplast ribonucleoproteins (40-51%). The 12RNP proteins were expressed in Escherichia coli bearing plasmids encoding glutathione S-transferase/12RNP fusion proteins and subjected to in vitro nucleic acid-binding assay. Both 12RNP1 and 12RNP2 bind to RNA homopolymers poly(U) and poly(G), indicating that they might be RNA-binding proteins. This is the first example of such proteins in prokaryotes. The 12RNP1 and 12RNP2 genes are transcribed as monocistronic mRNAs and the steady-state mRNA level of 12RNP1 is over 20-fold than that of 12RNP2. Due to the easiness of genetic manipulations the cyanobacterium will provide an excellent system to analyze the function of not only cyanobacterial but also plant RNA-binding proteins.
Full text
PDF

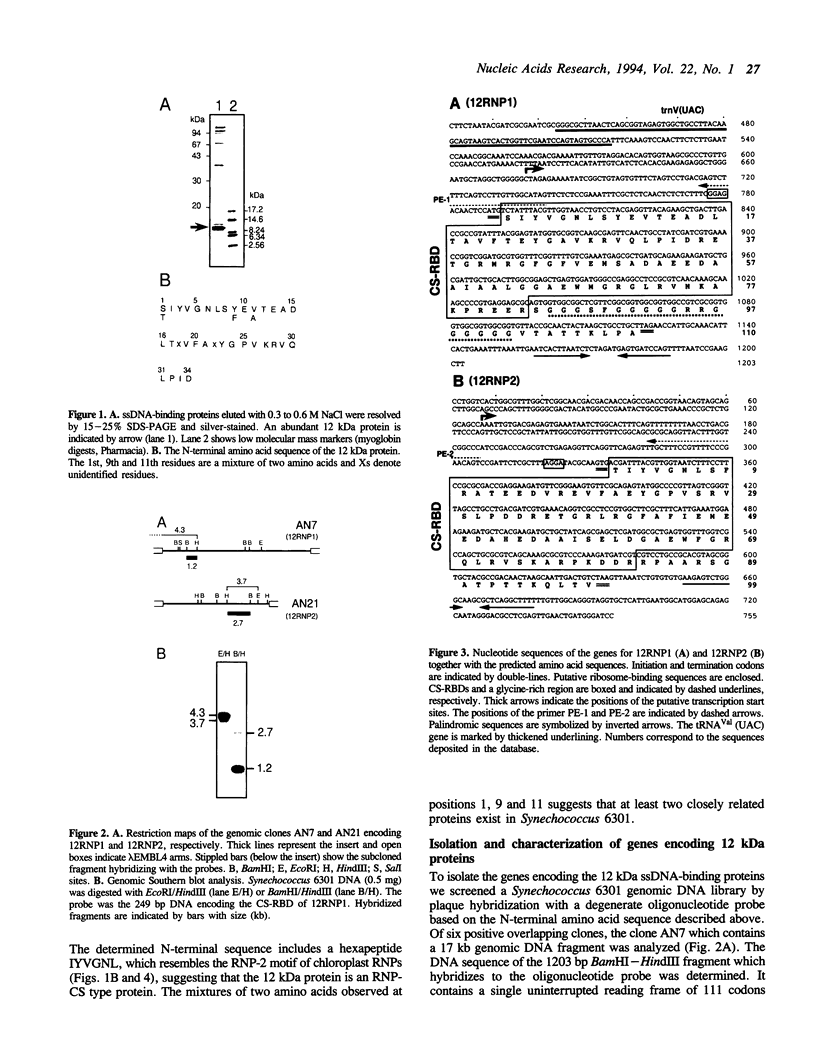

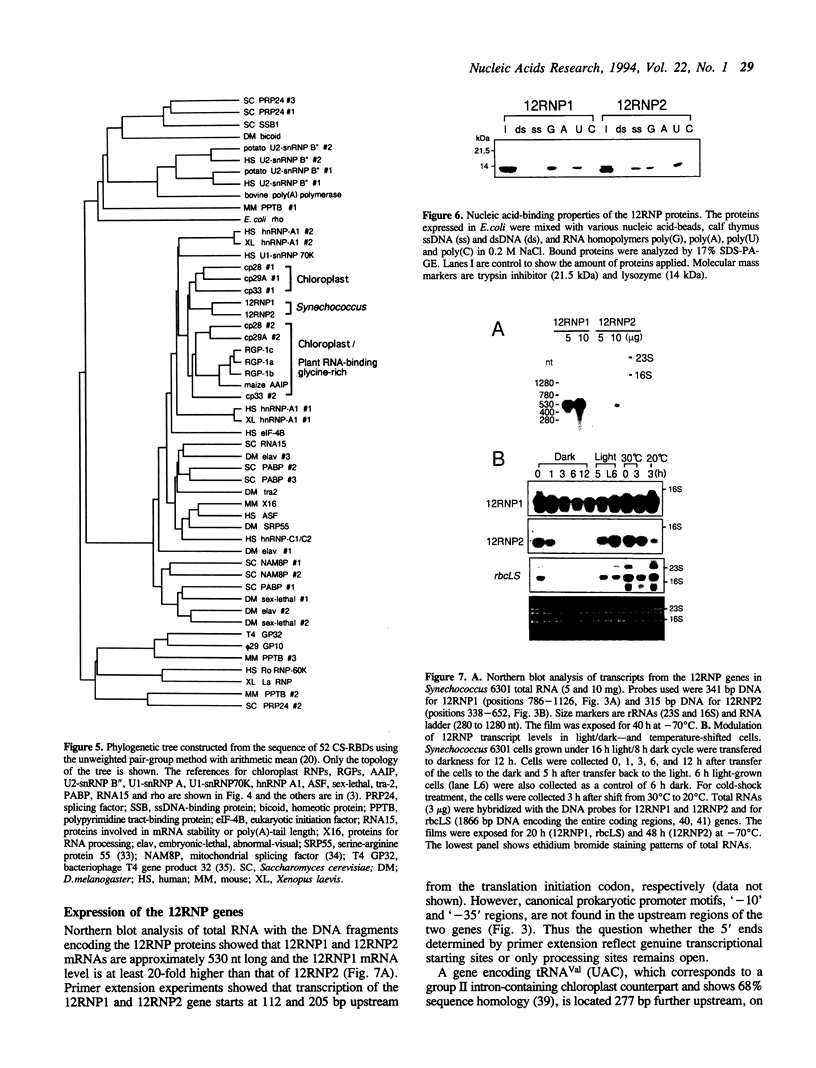


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amrein H., Gorman M., Nöthiger R. The sex-determining gene tra-2 of Drosophila encodes a putative RNA binding protein. Cell. 1988 Dec 23;55(6):1025–1035. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90247-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell L. R., Maine E. M., Schedl P., Cline T. W. Sex-lethal, a Drosophila sex determination switch gene, exhibits sex-specific RNA splicing and sequence similarity to RNA binding proteins. Cell. 1988 Dec 23;55(6):1037–1046. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90248-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brand S. N., Tan X., Widger W. R. Cloning and sequencing of the petBD operon from the cyanobacterium Synechococcus sp. PCC 7002. Plant Mol Biol. 1992 Nov;20(3):481–491. doi: 10.1007/BF00040607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cobianchi F., Karpel R. L., Williams K. R., Notario V., Wilson S. H. Mammalian heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein complex protein A1. Large-scale overproduction in Escherichia coli and cooperative binding to single-stranded nucleic acids. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jan 15;263(2):1063–1071. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook W. B., Walker J. C. Identification of a maize nucleic acid-binding protein (NBP) belonging to a family of nuclear-encoded chloroplast proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Jan 25;20(2):359–364. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.2.359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deno H., Kato A., Shinozaki K., Sugiura M. Nucleotide sequences of tobacco chloroplast genes for elongator tRNAMet and tRNAVal (UAC): the tRNAVal (UAC) gene contains a long intron. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Dec 11;10(23):7511–7520. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.23.7511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreyfuss G., Matunis M. J., Piñol-Roma S., Burd C. G. hnRNP proteins and the biogenesis of mRNA. Annu Rev Biochem. 1993;62:289–321. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.62.070193.001445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ekwall K., Kermorgant M., Dujardin G., Groudinsky O., Slonimski P. P. The NAM8 gene in Saccharomyces cerevisiae encodes a protein with putative RNA binding motifs and acts as a suppressor of mitochondrial splicing deficiencies when overexpressed. Mol Gen Genet. 1992 May;233(1-2):136–144. doi: 10.1007/BF00587571. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ge H., Zuo P., Manley J. L. Primary structure of the human splicing factor ASF reveals similarities with Drosophila regulators. Cell. 1991 Jul 26;66(2):373–382. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90626-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein J., Pollitt N. S., Inouye M. Major cold shock protein of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(1):283–287. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.1.283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray M. W. The evolutionary origins of organelles. Trends Genet. 1989 Sep;5(9):294–299. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(89)90111-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gómez J., Sánchez-Martínez D., Stiefel V., Rigau J., Puigdomènech P., Pagès M. A gene induced by the plant hormone abscisic acid in response to water stress encodes a glycine-rich protein. Nature. 1988 Jul 21;334(6179):262–264. doi: 10.1038/334262a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirose T., Sugita M., Sugiura M. cDNA structure, expression and nucleic acid-binding properties of three RNA-binding proteins in tobacco: occurrence of tissue-specific alternative splicing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Aug 25;21(17):3981–3987. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.17.3981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keene J. D., Query C. C. Nuclear RNA-binding proteins. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1991;41:179–202. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60009-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenan D. J., Query C. C., Keene J. D. RNA recognition: towards identifying determinants of specificity. Trends Biochem Sci. 1991 Jun;16(6):214–220. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(91)90088-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovacs S. A., O'Neil J., Watcharapijarn J., Moe-Kirvan C., Vijay S., Silva V. Eubacterial components similar to small nuclear ribonucleoproteins: identification of immunoprecipitable proteins and capped RNAs in a cyanobacterium and a gram-positive eubacterium. J Bacteriol. 1993 Apr;175(7):1871–1878. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.7.1871-1878.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krisch H. M., Allet B. Nucleotide sequences involved in bacteriophage T4 gene 32 translational self-regulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Aug;79(16):4937–4941. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.16.4937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhsel M. G., Strickland R., Palmer J. D. An ancient group I intron shared by eubacteria and chloroplasts. Science. 1990 Dec 14;250(4987):1570–1573. doi: 10.1126/science.2125748. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar A., Williams K. R., Szer W. Purification and domain structure of core hnRNP proteins A1 and A2 and their relationship to single-stranded DNA-binding proteins. J Biol Chem. 1986 Aug 25;261(24):11266–11273. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Y. Q., Sugiura M. Nucleic acid-binding specificities of tobacco chloroplast ribonucleoproteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jun 11;19(11):2893–2896. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.11.2893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Y. Q., Sugiura M. Three distinct ribonucleoproteins from tobacco chloroplasts: each contains a unique amino terminal acidic domain and two ribonucleoprotein consensus motifs. EMBO J. 1990 Oct;9(10):3059–3066. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07502.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Y., Nagayoshi S., Sugita M., Sugiura M. Structure and expression of the tobacco nuclear gene encoding the 33 kDa chloroplast ribonucleoprotein. Mol Gen Genet. 1993 May;239(1-2):304–309. doi: 10.1007/BF00281632. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludevid M. D., Freire M. A., Gómez J., Burd C. G., Albericio F., Giralt E., Dreyfuss G., Pagès M. RNA binding characteristics of a 16 kDa glycine-rich protein from maize. Plant J. 1992 Nov;2(6):999–1003. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsudaira P. Sequence from picomole quantities of proteins electroblotted onto polyvinylidene difluoride membranes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 25;262(21):10035–10038. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattaj I. W. A binding consensus: RNA-protein interactions in splicing, snRNPs, and sex. Cell. 1989 Apr 7;57(1):1–3. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90164-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meng B. Y., Shinozaki K., Sugiura M. Genes for the ribosomal proteins S12 and S7 and elongation factors EF-G and EF-Tu of the cyanobacterium, Anacystis nidulans: structural homology between 16S rRNA and S7 mRNA. Mol Gen Genet. 1989 Mar;216(1):25–30. doi: 10.1007/BF00332226. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minvielle-Sebastia L., Winsor B., Bonneaud N., Lacroute F. Mutations in the yeast RNA14 and RNA15 genes result in an abnormal mRNA decay rate; sequence analysis reveals an RNA-binding domain in the RNA15 protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jun;11(6):3075–3087. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.6.3075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohamed A., Jansson C. Influence of light on accumulation of photosynthesis-specific transcripts in the cyanobacterium Synechocystis 6803. Plant Mol Biol. 1989 Dec;13(6):693–700. doi: 10.1007/BF00016024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murayama Y., Matsubayashi T., Sugita M., Sugiura M. Purification of chloroplast elongation factor Tu and cDNA analysis in tobacco: the existence of two chloroplast elongation factor Tu species. Plant Mol Biol. 1993 Aug;22(5):767–774. doi: 10.1007/BF00027363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nadler S. G., Merrill B. M., Roberts W. J., Keating K. M., Lisbin M. J., Barnett S. F., Wilson S. H., Williams K. R. Interactions of the A1 heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein and its proteolytic derivative, UP1, with RNA and DNA: evidence for multiple RNA binding domains and salt-dependent binding mode transitions. Biochemistry. 1991 Mar 19;30(11):2968–2976. doi: 10.1021/bi00225a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pandolfo M., Valentini O., Biamonti G., Rossi P., Riva S. Large-scale purification of hnRNP proteins from HeLa cells by affinity chromatography on ssDNA-cellulose. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Jan 2;162(1):213–220. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb10563.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinkham J. L., Platt T. The nucleotide sequence of the rho gene of E. coli K-12. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jun 11;11(11):3531–3545. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.11.3531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Query C. C., Bentley R. C., Keene J. D. A common RNA recognition motif identified within a defined U1 RNA binding domain of the 70K U1 snRNP protein. Cell. 1989 Apr 7;57(1):89–101. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90175-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riva S., Morandi C., Tsoulfas P., Pandolfo M., Biamonti G., Merrill B., Williams K. R., Multhaup G., Beyreuther K., Werr H. Mammalian single-stranded DNA binding protein UP I is derived from the hnRNP core protein A1. EMBO J. 1986 Sep;5(9):2267–2273. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04494.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth M. B., Zahler A. M., Stolk J. A. A conserved family of nuclear phosphoproteins localized to sites of polymerase II transcription. J Cell Biol. 1991 Nov;115(3):587–596. doi: 10.1083/jcb.115.3.587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sachs A. B., Bond M. W., Kornberg R. D. A single gene from yeast for both nuclear and cytoplasmic polyadenylate-binding proteins: domain structure and expression. Cell. 1986 Jun 20;45(6):827–835. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90557-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schindelin H., Marahiel M. A., Heinemann U. Universal nucleic acid-binding domain revealed by crystal structure of the B. subtilis major cold-shock protein. Nature. 1993 Jul 8;364(6433):164–168. doi: 10.1038/364164a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuster G., Gruissem W. Chloroplast mRNA 3' end processing requires a nuclear-encoded RNA-binding protein. EMBO J. 1991 Jun;10(6):1493–1502. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07669.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinozaki K., Sugiura M. The gene for the small subunit of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase is located close to the gene for the large subunit in the cyanobacterium Anacystis nidulans 6301. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Oct 25;11(20):6957–6964. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.20.6957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinozaki K., Yamada C., Takahata N., Sugiura M. Molecular cloning and sequence analysis of the cyanobacterial gene for the large subunit of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):4050–4054. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.4050. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sillekens P. T., Habets W. J., Beijer R. P., van Venrooij W. J. cDNA cloning of the human U1 snRNA-associated A protein: extensive homology between U1 and U2 snRNP-specific proteins. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 1;6(12):3841–3848. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02721.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson G. G., Vaux P., Clark G., Waugh R., Beggs J. D., Brown J. W. Evolutionary conservation of the spliceosomal protein, U2B''. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Oct 11;19(19):5213–5217. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.19.5213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smart L. B., McIntosh L. Expression of photosynthesis genes in the cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803: psaA-psaB and psbA transcripts accumulate in dark-grown cells. Plant Mol Biol. 1991 Nov;17(5):959–971. doi: 10.1007/BF00037136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. B., Johnson K. S. Single-step purification of polypeptides expressed in Escherichia coli as fusions with glutathione S-transferase. Gene. 1988 Jul 15;67(1):31–40. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90005-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomioka N., Sugiura M. The complete nucleotide sequence of a 16S ribosomal RNA gene from a blue-green alga, Anacystis nidulans. Mol Gen Genet. 1983;191(1):46–50. doi: 10.1007/BF00330888. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willimsky G., Bang H., Fischer G., Marahiel M. A. Characterization of cspB, a Bacillus subtilis inducible cold shock gene affecting cell viability at low temperatures. J Bacteriol. 1992 Oct;174(20):6326–6335. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.20.6326-6335.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ye L. H., Li Y. Q., Fukami-Kobayashi K., Go M., Konishi T., Watanabe A., Sugiura M. Diversity of a ribonucleoprotein family in tobacco chloroplasts: two new chloroplast ribonucleoproteins and a phylogenetic tree of ten chloroplast RNA-binding domains. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Dec 11;19(23):6485–6490. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.23.6485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ye L., Sugiura M. Domains required for nucleic acid binding activities in chloroplast ribonucleoproteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Dec 11;20(23):6275–6279. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.23.6275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]