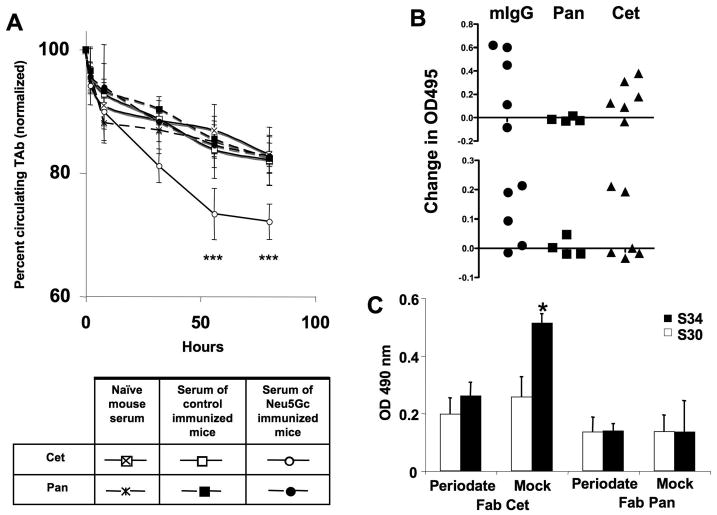
Figure 2. Effects of anti-Neu5Gc antibodies on the kinetics of therapeutic antibodies in mice with a human-like Neu5Gc-deficiency, levels of anti-Neu5Gc IgG in mice after injections of the therapeutic antibodies, and binding of IgG anti-Neu5Gc antibodies from whole human serum to Neu5Gc on the Fab fragment of Cetuximab.
(A) Cmah null mice were first injected i.v. with the therapeutic antibodies (TAbs), namely Cetuximab (Cet) or Panitumumab (Pan), and mouse serum from Cmah null mice containing anti-Neu5Gc antibodies (or serum from naïve mice or control immunized mice) was then passively transferred by IP injection. Mice were bled periodically after the passive transfer of mouse serum. Concentration of Cet and Pan in the isolated sera was determined by Sandwich ELISA. Absorbance was measured at 495 nm. The Y axis starts at 60%, in order to better display the difference in kinetics. ***p <0.001, Unpaired Two-tailed t-test. (B) Cmah null mice were injected i.v. with Cet or Pan weekly and were bled initially, and after the 3rd i.v. injection. In order to detect Neu5Gc specific antibodies by ELISA, wells were coated with human (Neu5Gc-deficient) and chimpanzee (Neu5Gc-positive) serum glycoproteins (Upper Panel), or alternatively with human or bovine fibrinogen (Lower Panel). Data were obtained in triplicate. (C) Fab fragments of Cet and Pan were isolated using the Pierce® Fab Preparation Kit according to the manufacturer's manual. Fab fragments (1 μg/well) were used as target molecules in ELISA. Sialic acid specific binding was determined with sodium metaperiodate treatment. Wells were then blocked and incubated with human sera (S30 and S34 with low and high anti-Neu5Gc IgG titers, respectively, from Ref. 11). Binding of human IgG was detected by using anti-human IgG-Fc. The absorbance was measured at 490 nm and ELISA samples were studied in triplicate. *= p <0.05. Paired Two-tailed t-test.